Watch 02: April 2022
The HIV/HCV Co-Infection Watch is a project of the Community Access National Network (CANN) designed to research, monitor and report on HIV and Hepatitis C (HCV) co-infection in the United States. The April 2022 Watch includes timely updates herein. To read the project disclaimer and/or methodology, CLICK HERE.
1. FINDINGS
The following is a summary of the key findings for April 2022:
AIDS Drug Assistance Programs:
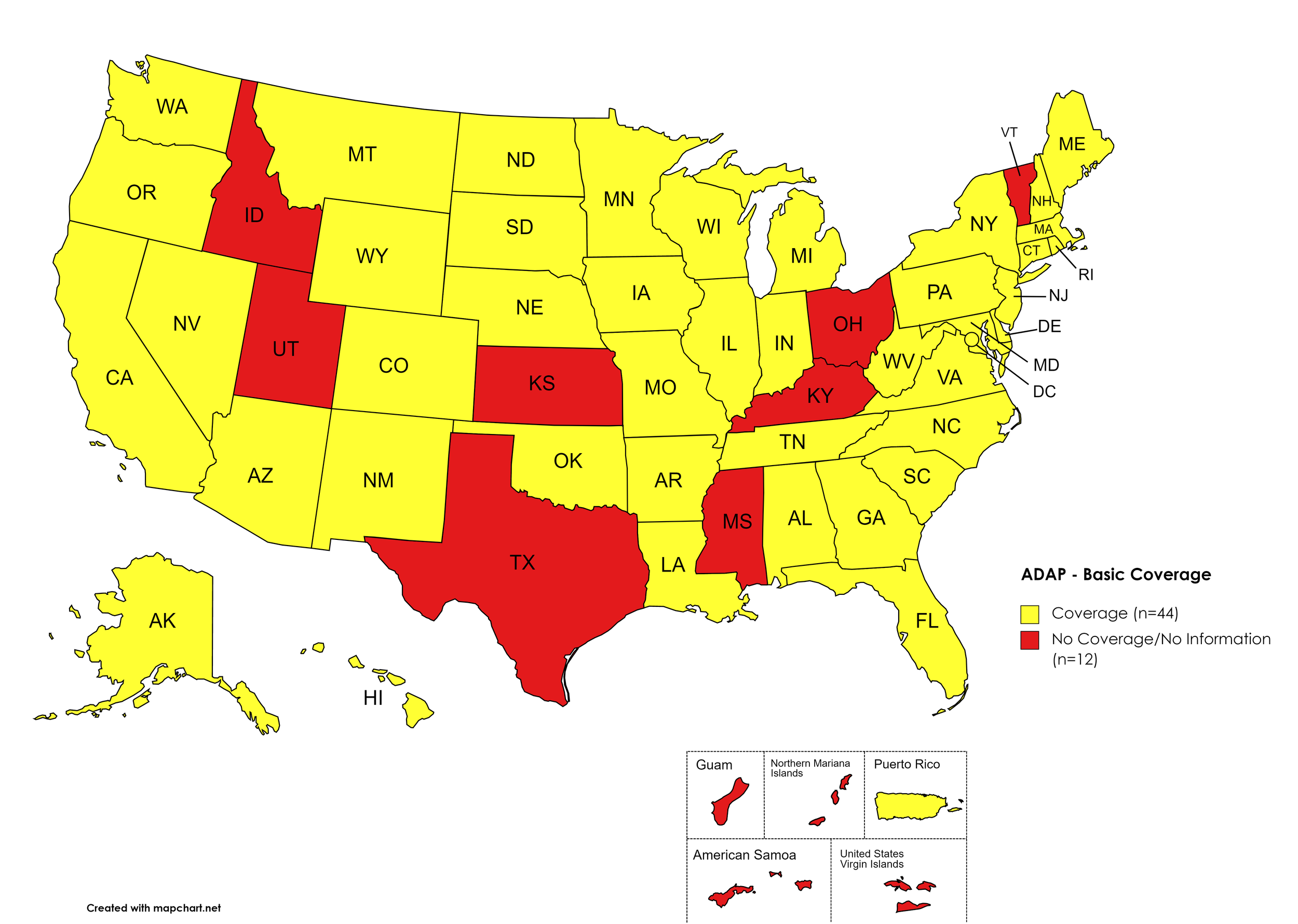
There are 56 State and Territorial AIDS Drug Assistance Programs (ADAPs) in the United States, 48 of which offer some form of coverage for Hepatitis C (HCV) treatment. Of those programs, 46 have expanded their HCV coverage to include the Direct-Acting Antiviral (DAA) regimens that serve as the current Standard of Care (SOC) for Hepatitis C treatment. Two (2) programs offer only Basic Coverage and 8 programs offer No Coverage. Two (2) programs cover only a single Direct-Acting Antiviral. Three (3) territories – American Samoa, Marshall Islands, and Northern Mariana Islands – are not accounted for in this data. A state-by-state Drug Formulary breakdown of coverage is included in the April 2022 Updates, with accompanying drug-specific maps in Figures 1 – 10.
Medicaid Programs:
There are 59 State and Territorial Medicaid programs in the United States, and data is represented for all fifty (50) states and the District of Columbia. As of October 01, 2016, all 50 states and the District of Columbia offer Expanded Coverage. A state-by-state PDL breakdown of coverage is included in the April 2022 Updates, with accompanying drug-specific maps in Figures 11 – 20.
Harm Reduction Programs:
Every State and Territory in the United States currently provides funding for low-income people living with substance abuse issues to enter state-funded rehabilitation services (National Center for Biotechnology Information, n.d.). Forty-four (44) States, the District of Columbia and three (3) Territories currently have Syringe Services Programs (SSPs) in place, regardless of the legality. Fifty (50) States and the District of Columbia have expanded access to Naloxone to avert opioid drug overdoses. Fifty (50) States and the District of Columbia have Good Samaritan laws or statutes that provide some level of protection for those rendering emergency services during drug overdoses. Forty-seven (47) States, the District of Columbia, and Guam make reporting to Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs (PDMPs) mandatory, requiring physicians and/or pharmacists to report prescriptions written or filled to a state agency for monitoring. Fifty (50) States and the District of Columbia have Opioid-Specific Doctor Shopping Laws preventing patients from attempting to receive multiple prescriptions from numerous physicians, and/or from withholding information in order to receive prescriptions. Forty-five (45) states and the District of Columbia mandate a Physical Exam Requirement in order for patients to receive a prescription for opioid drugs. Thirty-Five (35) states have in place an ID Requirement mandating that people filling opioid prescriptions present a state-issued ID prior to receiving their prescription. Forty-five (45) states and the District of Columbia require prescribing physicians to attend mandatory and continuing opioid prescribing education sessions. Forty-seven (47) states and the District of Columbia have Medicaid doctor/pharmacy Lock-In programs that require patients to receive prescriptions from a single physician and/or fill prescriptions from a single pharmacy. A state-by-state program breakdown is included in the April 2022 Updates, with accompanying drug-specific maps in Figures 21-29.
2. AIDS DRUG ASSISTANCE PROGRAMS (ADAPs) & HCV THERAPIES
Of the 56 respective State and Territorial ADAPs, only 8 (KS, KY, OH, UT, VT, GU, PW, VI) do not offer any coverage for HCV drug therapies. States whose formularies are not available on the state-run website have been checked against the most recent National Alliance of State and Territorial AIDS Directors (NASTAD) formulary database (last updated January 1, 2022). The data presented are current as of April 15, 2022.
April 2022 Updates:
Basic Coverage
States with Basic HCV Medications Coverage: AL, AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, IL, IN, IA, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MO, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, SD, TN, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Basic HCV Medications Coverage: ID, KS, KY, MS, OH, TX, UT, VT
Territories with Basic HCV Medications Coverage: P.R.
Figure 1. April 2022 ADAP Coverage - Basic HCV Medications
Map Key: Yellow = Basic HCV Medication Coverage; Red = No Basic HCV Medication Coverage/No Information regarding Basic HCV Medication Coverage
Sovaldi
States with Sovaldi Coverage: AZ, CA, CO, GA, HI, IL, IN, IA, LA, ME, MD, MA, MN, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, ND, OK, OR, PA, SD, VA, WA, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Sovaldi Coverage: AL, AK, AR, CT, DE, FL, ID, KS, KY, MI, MS, MO, MT, NY, NC, OH, RI, SC, TN, TX, UT, VT, WV
Territories with Sovaldi Coverage: P.R.
Figure 2. April 2022 ADAP Coverage - Sovaldi
Map Key: Yellow = Sovaldi Coverage; Red = No Sovaldi Coverage/No Information regarding Sovaldi Coverage
Harvoni
States with Harvoni Coverage: AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NC, ND, OK, OR, PA, SD, TN, VA, WA, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Harvoni Coverage: AL, AK, KS, KY, MO, MT, NY, OH, RI, SC, TX, UT, VT, WV
Territories with Harvoni Coverage: P.R.
Figure 3. April 2022 ADAP Coverage - Harvoni
Map Key: Yellow = Harvoni Coverage; Red = No Harvoni Coverage/No Information regarding Harvoni Coverage
Zepatier
States with Zepatier Coverage: AL, AZ, AR, CA, CO, FL, GA, HI, IL, IA, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OR, PA, SD, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Zepatier Coverage: AK, CT, DE, ID, IN, KS, KY, MO, MT, OH, OK, RI, SC, TN, TX, UT, VT
Territories with Zepatier Coverage: P.R.
Figure 4. April 2022 ADAP Coverage - Zepatier
Map Key: Yellow = Zepatier Coverage; Red = No Zepatier Coverage/No Information regarding Zepatier Coverage
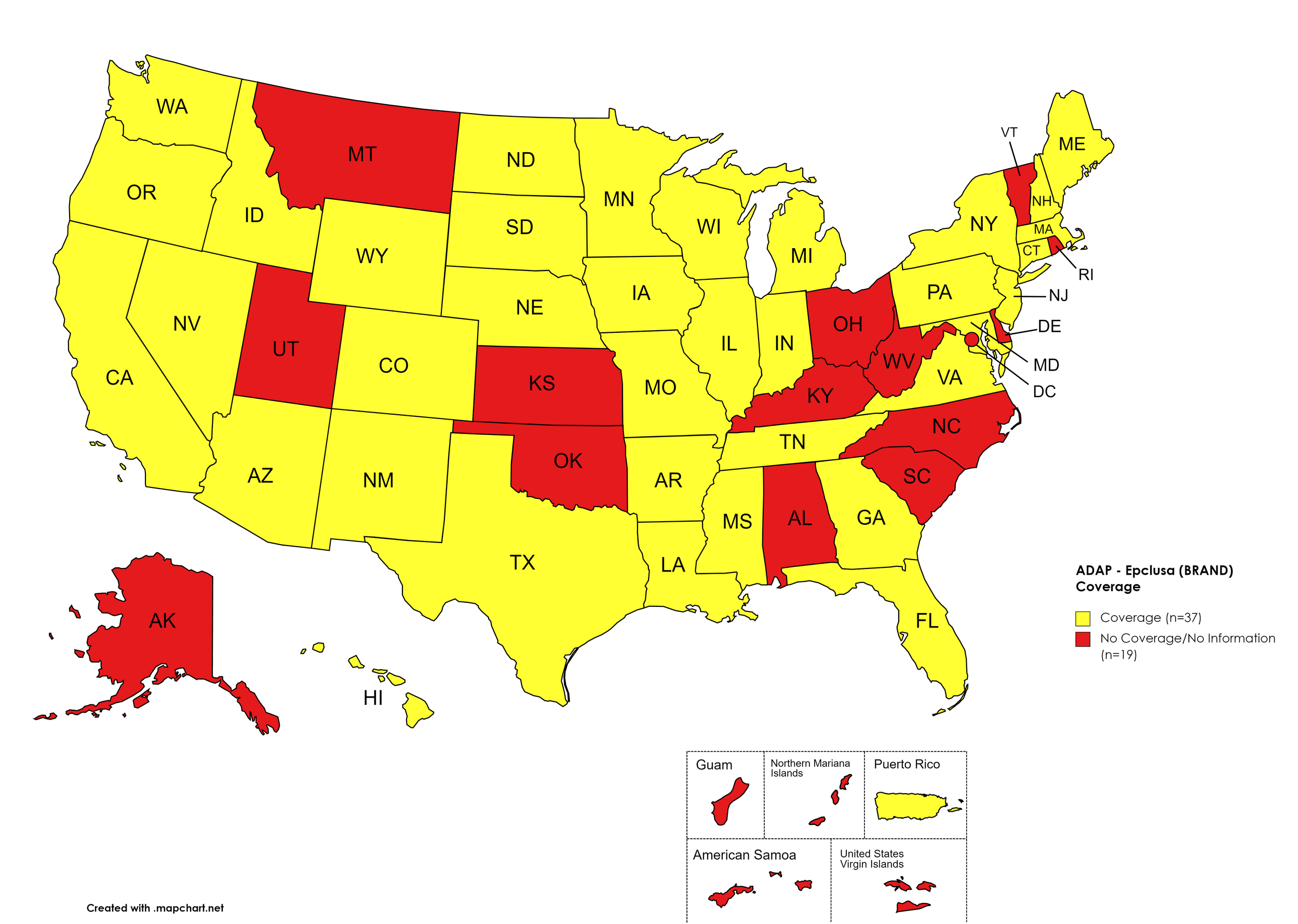
Epclusa
States with Epclusa Coverage: AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, MO, NE, NY, NV, NH, NJ, NM, ND, OR, PA, SD, TN, TX, VA, WA, WI, WY
States without Epclusa Coverage: AL, AK, DE, KS, KY, MT, NC, OH, OK, RI, SC, UT, VT, WV, D.C.
Territories with Epclusa Coverage: P.R.
Figure 5. April 2022 ADAP Coverage - Epclusa
Map Key: Yellow = Epclusa Coverage; Red = No Epclusa Coverage/No Information regarding Epclusa Coverage
Vosevi
States with Vosevi Coverage: CA, CT, FL, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, LA, MD, MA, MN, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, ND, OR, SD, TN, WA, WY
States without Vosevi Coverage: AL, AK, AZ, AR, CO, DE, GA, KS, KY, ME, MI, MS, MO, MT, NY, NC, OH, OK, PA, RI, SC, TX, UT, VT, VA, WV, WI, D.C.
Territories with Vosevi Coverage: P.R.
Figure 6. April 2022 ADAP Coverage - Vosevi
Map Key: Yellow = Vosevi Coverage; Red = No Vosevi Coverage/No Information regarding Vosevi Coverage
Mavyret
States with Mavyret Coverage: AL, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, MO, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OR, PA, SD, TN, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Mavyret Coverage: AK, DE, KS, KY, OH, OK, RI, SC, TX, UT, VT
Territories with Mavyret Coverage: P.R.
Figure 7. April 2022 ADAP Coverage - Mavyret
Map Key: Yellow = Mavyret Coverage; Red = No Mavyret Coverage/No Information regarding Mavyret Coverage
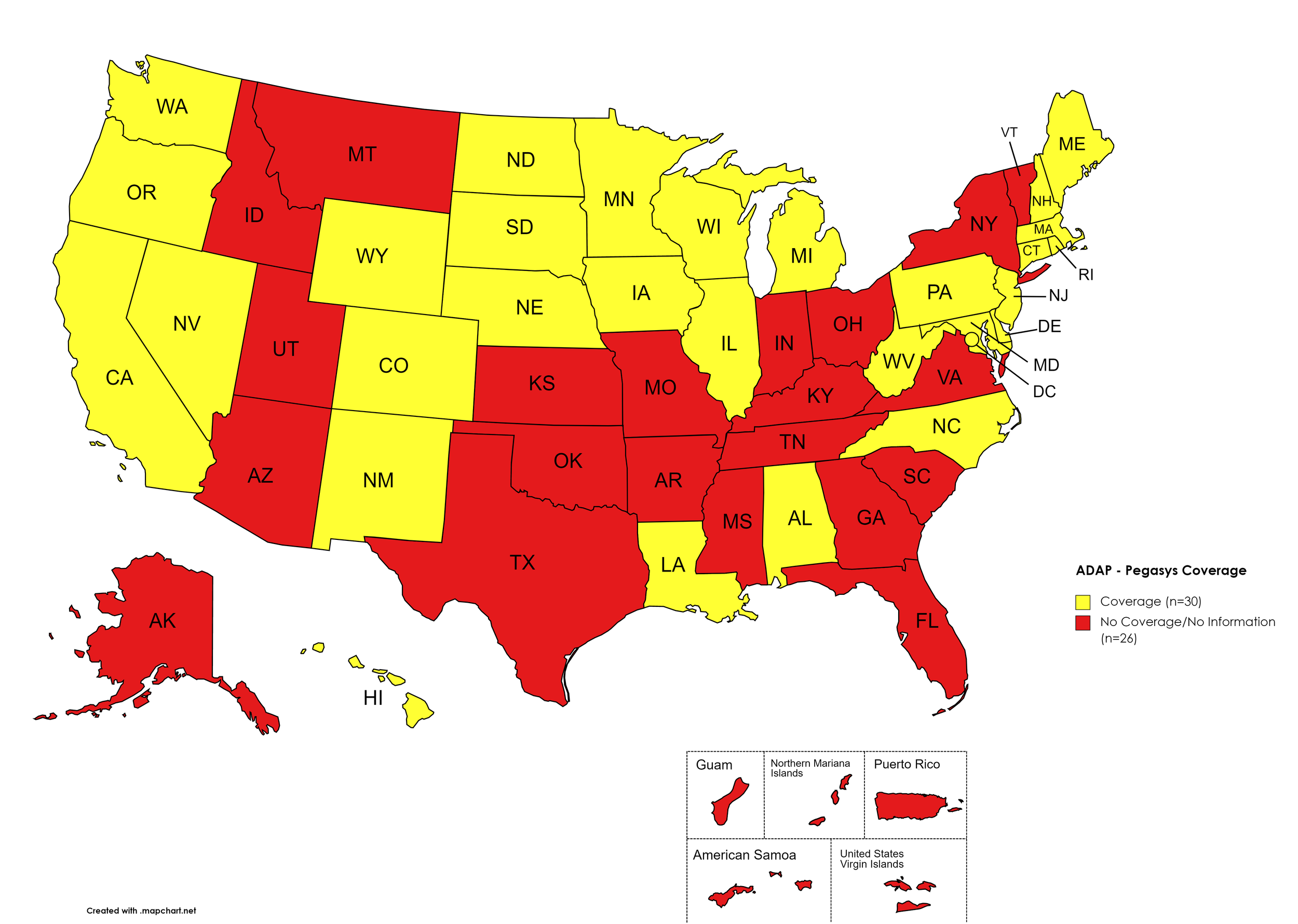
Pegasys
States with Pegasys Coverage: AL, CA, CO, CT, DE, HI, IL, IA, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NC, ND, OR, PA, RI, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Pegasys Coverage: AK, AZ, AR, FL, GA, ID, IN, KS, KY, MS, MO, MT, NY, OH, OK, SC, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA
Territories with Pegasys Coverage: None/Unknown
Figure 8. April 2022 ADAP Coverage - Pegasys
Map Key: Yellow = Pegasys Coverage; Red = No Pegasys Coverage/No Information regarding Pegasys Coverage
Harvoni (generic)
States with Harvoni (generic) Coverage: AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, FL, IL, IA, ME, MD, MA, MN, MS, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NC, ND, OK, OR, PA, SD, TN, WA, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Harvoni (generic)Coverage: AL, AK, DE, GA, HI, ID, IN, KS, KY, LA, MI, MO, MT, NY, OH, RI, SC, TX, UT, VT, VA, WV
Territories with Harvoni (generic) Coverage: P.R.
Figure 9. April 2022 ADAP Coverage - Harvoni (Generic)
Map Key: Yellow = Harvoni (Generic) Coverage; Red = No Harvoni (Generic) Coverage/No Information regarding Harvoni (Generic) Coverage
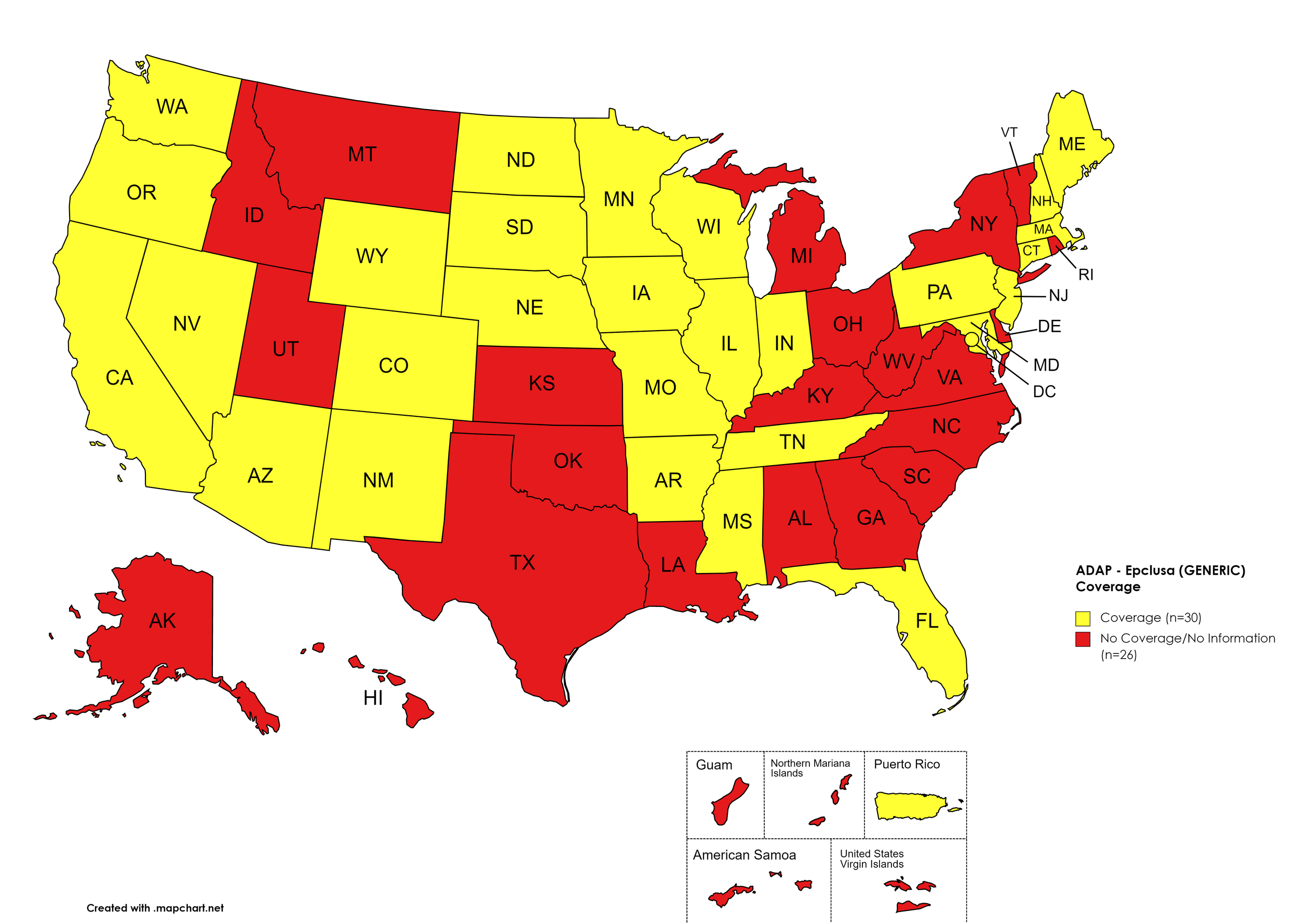
Epclusa (generic)
States with Epclusa (generic) Coverage: AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, FL, IL, IN, IA, ME, MD, MA, MN, MS, MO, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, ND, OR, PA, SD, TN, WA, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Epclusa (generic) Coverage: AL, AK, DE, GA, HI, ID, KS, KY, LA, MI, MT, NY, NC, OH, OK, RI, SC, TX, UT, VT, VA, WV
Territories with Epclusa (generic) Coverage: P.R.
Figure 10. April 2022 ADAP Coverage - Epclusa (generic)
Map Key: Yellow = Epclusa (generic) Coverage; Red = No Epclusa (generic) Coverage/No Information regarding Epclusa (generic) Coverage
April 2022 Notes:
States with Open Formularies: IL, IA, MA, MN, NE, NH, NJ, NM, ND, OH, OR, WA, WY
N.B. – Although Ohio is listed by NASTAD as having an open formulary, both NASTAD’s ADAP Formulary Database and Ohio’s ADAP website indicates that the state does not offer any treatment for HCV
N.B. – Although North Dakota has adopted an open formulary, they provide only co-pay and deductible assistance for HCV medications
N.B. – Wyoming's ADAP Open Formulary document, the following disclaimer related to HCV is made: Hepatitis C treatment medications (i.e. Harvoni, Sovaldi, Ribavirin, Zepatier, Epclusa) must be prior authorized. To be eligible, clients must have applied for prior authorization from their insurance plan and the WY ADAP Hepatitis C Treatment checklist must be completed and signed by the provider and client
Colorado offers five coverage options – Standard ADAP, HIV Medical Assistance Program (HMAP), Bridging the Gap Colorado (BTGC), HIV Insurance Assistance Program (HIAP), and Supplemental Wrap Around Program (SWAP). ‘Yes’ indications in Figure 1. for Colorado denote that at least one of these programs offers coverage for each respective drug. The Standard ADAP Formulary covers medications only if funds are available to do so
Colorado has expanded coverage to include all generic HCV medications
Georgia notes the following: “Georgia ADAP Hepatitis C Program is currently on HOLD until future funding is available. Please utilize Patient Assistance Programs (PAP’s) for Hepatitis C medications.”
Louisiana’s ADAP (Louisiana Health Access Program – LA HAP) offers two coverage options – Uninsured (Louisiana Drug Assistance Program – L-DAP) and Insured (Health Insurance Program – HIP). HIP pays for the cost of treatment only if the client’s primary insurance covers the drug under its formulary
Texas has reduced coverage of all HCV medications except Epclusa (brand)
Idaho has added coverage for Harvoni (BRAND), Epclusa (BRAND), and Vosevi - the first inclusion of HCV medications for ID’s ADAP
3. MEDICAID PROGRAMS & HCV THERAPIES
All 50 states and the District of Columbia continue to offer some form of HCV coverage. All 50 states and the District of Columbia have expanded their Preferred Drug Lists to include at least one HCV Direct Acting Agent (DAA).
April 2022 Updates:
Basic Coverage
States with Basic HCV Medications Coverage: AZ, AK, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OR, PA, RI, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, WA, WV, WI, D.C.
States without Basic HCV Medications Coverage: AL, KS, MO, OK, SC, VA, WY
Figure 11. April 2022 Medicaid Coverage - Basic HCV Medications
Map Key: Blue = Basic HCV Medication Coverage; Yellow = No Basic HCV Medication Coverage/No Information regarding Basic HCV Medication Coverage
Sovaldi
States with Sovaldi Coverage: AR, CA, CO, DE, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, MO, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, PA, RI, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Sovaldi Coverage: AL, AK, AZ, CT, FL, NM, OR, SC
Figure 12. April 2022 Medicaid Coverage - Sovaldi
Map Key: Blue = Sovaldi Coverage; Yellow = No Sovaldi Coverage/No Information regarding Sovaldi Coverage
Harvoni
States with Harvoni Coverage: AL, AR, CA, CO, DE, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, MO, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, PA, RI, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Harvoni Coverage: AK, AZ, CT, FL, NM, OR, SC
Figure 13. April 2022 Medicaid Coverage - Harvoni
Map Key: Blue = Harvoni Coverage; Yellow = No Harvoni Coverage/No Information regarding Harvoni Coverage
Zepatier
States with Zepatier Coverage: AL, AR, CA, CO, DE, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, MO, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NY, NC, ND, OH, PA, RI, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Zepatier Coverage: AK, AZ, CT, FL, NM, OK, OR, SC
Figure 14. April 2022 Medicaid Coverage - Zepatier
Map Key: Blue = Zepatier Coverage; Yellow = No Zepatier Coverage/No Information regarding Zepatier Coverage
Epclusa
States with Epclusa Coverage: AL, AR, CA, CO, GA, HI, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, LA, MA, ME, MD, MI, MN, MS, MO, MT, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OR, PA, RI, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Epclusa Coverage: AK, AZ, CT, DE, FL, ID, OK NE, SC
Figure 15. April 2022 Medicaid Coverage - Epclusa
Map Key: Blue = Epclusa Coverage; Yellow = No Epclusa Coverage/No Information regarding Epclusa Coverage
Vosevi
States with Vosevi Coverage: AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, MO, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NY, NC, ND, OH, OR, PA, RI, SC, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Vosevi Coverage: AL, AK, AZ, NM, OK
Figure 16. April 2022 Medicaid Coverage - Vosevi
Map Key: Blue = Vosevi Coverage; Yellow = No Vosevi Coverage/No Information regarding Vosevi Coverage
Mavyret
States with Mavyret Coverage: AL, AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, MO, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
Figure 17. April 2022 Medicaid Coverage - Mavyret
Map Key: Blue = Mavyret Coverage; Yellow = No Mavyret Coverage/No Information regarding Mavyret Coverage
Pegasys
States with Pegasys Coverage: AK, AZ, CA, CT DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, OH, OR, PA, RI, SD, TN, TX, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, D.C.
States without Pegasys Coverage: AL, AR, CO, KS, MO, ND, OK, SC, UT, WY
Figure 18. April 2022 Medicaid Coverage - Pegasys
Map Key: Blue = Pegasys Coverage; Yellow = No Pegasys Coverage/No Information regarding Pegasys Coverage
Harvoni (generic)
States with Harvoni (generic) Coverage: AL, AR, CA, CO, DE, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, MO, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, PA, RI, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, D.C.
States without Harvoni (generic) Coverage: AK, AZ, CT, FL, KS, NM, OR, SC, WY
Figure 19. April 2022 Medicaid Coverage - Harvoni (generic)
Map Key: Blue = Harvoni (generic) Coverage; Yellow = No Harvoni (generic) Coverage/No Information regarding Harvoni (generic) Coverage
Epclusa (generic)
States with Epclusa (generic) Coverage: AL, AZ, AR, CA, CO, DE, FL, GA, HI, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, LA, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, MO, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OR, PA, RI, SC, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Epclusa (generic) Coverage: AK, CT, ID, ME, OK
Figure 20. April 2022 Medicaid Coverage - Epclusa (generic)
Map Key: Blue = Epclusa (generic) Coverage; Yellow = No Epclusa (generic) Coverage/No Information regarding Epclusa (generic) Coverage
April 2022 Notes:
The follow states’ Medicaid programs offer multiple coverage plans for their respective Medicaid clients. The plan highlighted in bold typeface represents the most comprehensive plan with the most drugs covered in the respective state:
Hawaii – (1.) Advantage Plus; (2.) QUEST Integration
New Jersey – (1.) Aetna; (2.) AmeriGroup NJ; (3.) Horizon NJ Health; (4.) UnitedHealthcare of New Jersey; (5.) WellCare
New Mexico – (1.) BlueCross BlueShield of New Mexico; (2.) Presbyterian Centennial Care; (3) Western Sky Community Care
Kentucky has a Unified Medicaid Formulary
Louisiana has a Unified Medicaid Formulary
Ohio – Ohio has a Unified Medicaid Formulary that applies to all MCOs
Georgia and Maryland have added Epclusa (BRAND) to their PDLs
Oregon has added Vosevi to its PDL
Oklahoma has added Mavyret to its PDL
Massachusetts and Wyoming have added Epclusa (generic) to their PDLs
No data is has been made available by the Medicaid programs in the U.S. Territories
*Medicaid coverage excludes patients from most drug manufacturer patient assistance programs (PAPs)
4. VETERANS PROGRAMS & HCV THERAPIES
The Veteran's Administration (VA) currently offers coverage for all HCV drugs. This is according to the most recent VA National Formulary, dated May 2021 (U.S. Dept. of V.A., 2021a). The VA Treatment Considerations and Choice of Regimen for HCV-Mono-Infected and HIV/HCV Co-Infected Patients, dated March 2021 (U.S. Dept. of V.A., 2021b) lists the following therapies as preferred treatments:
Abbreviations:
- CTP – Child-Turcotte-Pugh (score used to assess severity of cirrhosis)
- IU/mL – International Units Per Milliliter
- PEG-IFN/IFN – Peginterferon/Interferon
- RAS – Resistance-associated substitutions
Genotype 1:
Treatment-naïve without or with cirrhosis (CTP A):
Pangenotypic regimens
Mavyret: 3 tablets orally daily with food for 8 weeks; may consider 12 weeks in patients with poor prognostic factors
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily for 12 weeks
Non-pangenotypic regimens:
Zepatier: 1 tablet orally daily for 12 weeks if GT1a without baseline NS5A RAS or GT1b
Harvoni: 1 tablet orally daily
If HCV-noninfected, non-cirrhotic, and HCV RNA baseline <6 million IU/mL: 8 weeks
If cirrhotic, baseline HCV RNA ≥6 million IU/mL, HIV/HCV-co-infected, or African American: 12 weeks
Consider adding ribavirin in CTP A patients
Treatment-naïve with decompensated cirrhosis (CTP B or C):
Harvoni: 1 tablet orally daily + ribavirin (600 mg/day and increase by 200 mg/day every 2 weeks only as tolerated) for 12 weeks
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily + ribavirin (1000 mg/day - <75kg – or 1,200 mg daily - ≥75kg – orally daily in 2 divided doses with food) for 12 weeks; start at lower ribavirin doses as clinically indicated (e.g., baseline Hgb).
Treatment-experienced (NS5A- and SOF-naïve [e.g., failed PEG-IFN/RBV ± NS3/4A PI]) without or with cirrhosis (CTP A)
Pangenotypic regimens:
Mavyret: 3 tablets orally daily with food
If PEG-IFN/RBV-experienced: 8 weeks if non-cirrhotic or 12 weeks if cirrhotic
If NS3/4A PI + PEG-IFN/RBV-experienced: 12 weeks
Vosevi: 1 tablet orally daily for 12 weeks
Non-pangenotypic regimens
Zepatier: 1 tablet orally daily for 12 weeks if GT1b, or if failed only PEG-IFN/RBV and GT1a without baseline NS5A RAS
Harvoni: 1 tablet orally daily for 12 weeks
Treatment-experienced (NS5A-naïve and SOF-experienced) without or with cirrhosis (CTP A)
Mavyret: 3 tablets orally daily with food
If PEG-IFN/RBV + Sovaldi-experienced: 8 weeks if non-cirrhotic or 12 weeks if cirrhotic
If Olysio + Sovaldi-experienced: 12 weeks
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily for 12 weeks if GT1b
Vosevi: 1 tablet orally daily with food for 12 weeks if GT1a
Treatment-experienced (prior NS5A-containing regimen) without or with cirrhosis (CTP A)
Mavyret: 3 tablets orally daily with food for 16 weeks if failed only an NS5A inhibitor without NS3/4A PI (e.g., Harvoni)
Vosevi: 1 tablet orally daily with food for 12 weeks
Treatment-experienced with decompensated cirrhosis (CTP B or C)
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily + RBV; start at lower RBV doses as clinically indicated (e.g., baseline Hgb);
If NS5A-naïve: 12 weeks
If NS5A-experienced: 24 weeks; NOT FDA approved for 24 weeks
Genotype 2:
Treatment-naïve or treatment-experienced (PEG-IFN/IFN ± RBV or Sovaldi + RBV ± PEG-IFN) without or with cirrhosis (CTP A)
Mavyret: 3 tablets orally daily with food for 8 weeks; 12 weeks if CTP A and treatment-experienced or in patients with poor prognostic factors
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily for 12 weeks
Treatment-experienced (NS5A-experienced) without or with cirrhosis (CTP A)
Vosevi: 1 tablet orally daily with food for 12 weeks
Treatment-naïve or treatment-experienced patients with decompensated cirrhosis (CTP B or CTP C)
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily + ribavirin; start at lower ribavirin doses as clinically indicated (e.g., baseline Hgb)
If NS5A-naïve: 12 weeks
If NS5A-experienced: 24 weeks
Genotype 3:
Treatment-naïve without cirrhosis or with cirrhosis (CTP A)
Mavyret: 3 tablets orally daily with food for 8 weeks; may consider 12 weeks if cirrhotic or in patients with poor prognostic factors
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily for 12 weeks
If CTP A, test for NS5A RAS
Add ribavirin if Y93H RAS present
Treatment-experienced (PEG-IFN ± RBV or Sovaldi + RBV ± PEG-IFN) without or with cirrhosis (CTP A)
Mavyret: 3 tablets orally daily with food for 16 weeks
Treatment-experienced (NS5A-experienced) without or with cirrhosis (CTP A)
Vosevi: 1 tablet orally daily with food for 12 weeks
If CTP A, consider adding ribavirin (no supporting data)
Treatment-naïve or treatment-experienced with decompensated cirrhosis (CTP B or CTP C)
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily + ribavirin; start at lower ribavirin doses as clinically indicated (e.g., baseline Hgb)
If NS5A-naïve: 12 weeks
If NS5A-experienced: 24 weeks
Genotype 4:
Treatment-naïve without or with cirrhosis (CTP A)
Pangenotypic regimens
Mavyret: 3 tablets orally daily with food for 8 weeks; may consider 12 weeks in patients with poor prognostic factors
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily for 12 weeks
Non-pangenotypic regimens
Zepatier: 1 tablet orally daily for 12 weeks
Harvoni: 1 tablet orally daily for 12 weeks
Treatment-naïve with decompensated cirrhosis (CTP B or C)
Pangenotypic regimen
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily + RBV for 12 weeks; start at lower ribavirin doses as clinically indicated (e.g., baseline Hgb)
Non-pangenotypic regimen:
Harvoni: 1 tablet orally daily + ribavirin (600 mg/day and increase by 200 mg/day every 2 weeks only as tolerated) for 12 weeks
Treatment-experienced (Sovaldi-experienced and NS5A-naïve) without or with cirrhosis (CTP A)
Mavyret: 3 tablets orally daily with food for 8 weeks if NS3/4A PI-naïve without cirrhosis, and 12 weeks if NS3/4A PI-experienced or CTP A
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily + ribavirin for 12 weeks; start at lower ribavirin doses as clinically indicated (e.g., baseline Hgb)
Treatment-experienced (NS5A-experienced) without or with cirrhosis (CTP A)
Vosevi: 1 tablet orally daily with food for 12 weeks
Treatment-experienced with decompensated cirrhosis (CTP B or CTP C)
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily + ribavirin; start at lower ribavirin doses as clinically indicated (e.g., baseline Hgb)
If NS5A-naïve: 12 weeks
If NS5A-experienced: 24 weeks; NOT FDA approved for 24 weeks
5. PATIENT ASSISTANCE PROGRAMS
The drug manufacturers and various national nonprofit organizations offer a variation of patient assistance programs (PAPs) to assist patients in accessing treatments. They include:
Support Path (Gilead Sciences):
Financial Assistance
Provides Co-Pay Coupons for Sovaldi, Harvoni, Harvoni (Generic), Epclusa, Epclusa (Generic), and Vosevi
Co-Pay Coupons cover out-of-pocket costs up to 25% of the catalog price of a 12-week regimen (3 bottles/packages) of Sovaldi, Harvoni, Harvoni (Generic), Epclusa, Epclusa (Generic), or Vosevi
Excludes patients enrolled in Medicare Part D or Medicaid
Insurance Support
Researches and verifies patient’s benefits, and gives information they need about coverage options and policies
Explain Prior Authorization process and works with HCV Specialist’s office so they can submit PA forms to a patient’s insurance company
May be able to provide assistance with appeals process
Website: http://www.mysupportpath.com/
AbbVie Mavyret Co-Pay Savings Card:
Financial Assistance
Patient may be eligible to pay as little as $5
Excludes patients enrolled in Medicare Part D, Medicare Advantage, Medigap, Medicaid, TRICARE, Department of Defense, or Veterans Affairs programs)
NeedyMeds:
NeedyMeds Drug Discount Card
Designed to lower cost of prescription medications by up to 80% at participating pharmacies
NeedyMeds DOES NOT keep a list of prescription medications covered
No eligibility requirements
Patients CANNOT be enrolled in any insurance
CANNOT be used in combination with government healthcare programs, but CAN be used IN PLACE of program
CANNOT be combined with other offers
Website: http://ow.ly/fEJo309cJ7Z
The Assistance Fund:
Status: WAITLISTED
Requires provider referral
Copay assistance
Eligibility Criteria:
US citizen or permanent resident
Diagnosed with the disease for which you are applying
Prescribed an FDA-approved treatment for the disease
Have prescription coverage for the prescribed treatment
Meet financial eligibility criteria based upon household income and size
Patient Advocate Foundation Co-Pay Relief:
Status: CLOSED
Maximum award of $15,000
Eligibility Requirements:
Patient must be insured, and insurance must cover prescribed medication
Confirmed HCV diagnosis
Reside and receive treatment in the U.S.
Income falls below 400% of FPL with consideration of the Cost of Living Index (COLI) and the number in the household
Patient Access Network (PAN) Foundation:
Status: WAITLISTED
Co-Pay Assistance with a maximum award of $6,000
Patients may apply for a second grant during their eligibility period subject to availability of funding
Eligibility Requirements:
Must be being treated for HCV
Have insurance that covers HCV prescribed medication
Medication must be listed on PAN’s list of covered medications: https://www.panfoundation.org/index.php/en/patients/medications-covered
Income falls below 500% of FPL
Residing and receiving treatment in the U.S. (citizenship NOT required)
Website: https://www.panfoundation.org/index.php/en/patients/assistance-programs/hepatitis-c
HealthWell Foundation:
Status: OPEN
Co-Pay Assistance with a maximum award of $30,000
Minimum Co-Pay Reimbursement Amount: None
Minimum Premium Reimbursement Amount: None
Eligibility Requirements:
Must be being treated for HCV
Have insurance that covers HCV prescribed medication
Income falls below 500% of FPL
Receiving treatment in the U.S.
Website: https://www.healthwellfoundation.org/fund/hepatitis-c/
6. HARM REDUCTION PROGRAMS
Harm Reduction, as it relates to opioid abuse and HCV, are measures designed to serve as preventive or monitoring efforts in combating opioid prescription drug and heroin abuse, and as an effect, helping to prevent the spread of HCV and HIV. The Co-Infection Watch covers the following measures: Syringe Exchange, Expanded Naloxone Access, Good Samaritan Laws, Mandatory PDMP Reporting, Doctor Shopping Laws, Physical Exam Requirements, ID Requirements for Purchase, Required or Recommended Prescriber Education, and Lock-In Programs (Editor’s Note: Program descriptions provided herein).
April 2022 Updates:
Syringe Exchange
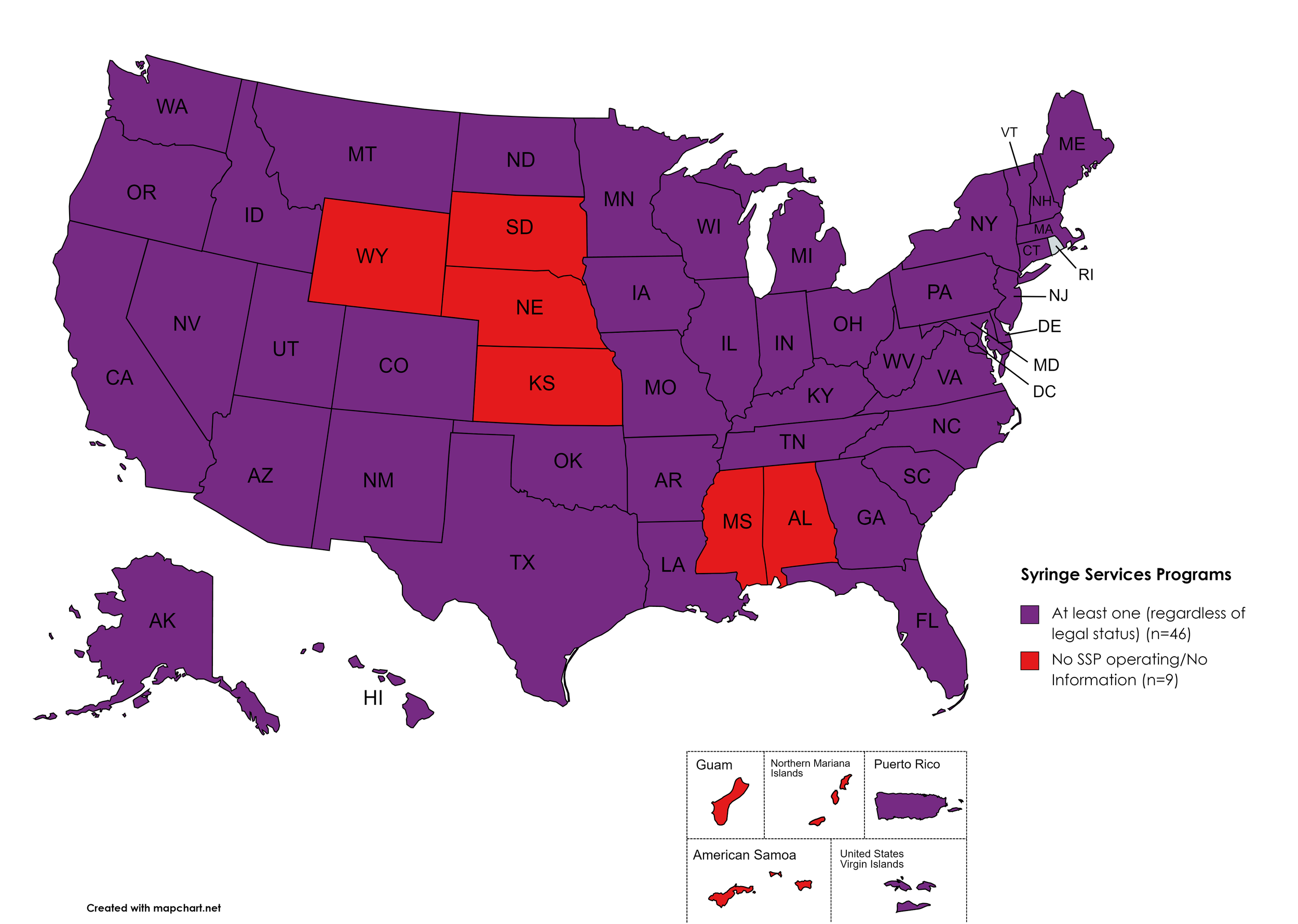
Syringe Services Programs (SSPs) exist to provide injection drug users (or those whose prescriptions require injection) with clean syringes and/or in exchange for used ones. (N.b. – states listed as "at least one SSP…” indicate only that a Syringe Services Program (SSP) exists within the state, regardless of the legality of SSPs under state law).
States with Syringe Exchange: AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MO, MT, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, D.C.
States without Syringe Exchange: AL, KS, MS, NE, SD, WY
Territories with Syringe Exchange: Puerto Rico, U.S. Virgin Islands
Figure 21. April 2022 Syringe Exchange Coverage
Map Key: Purple = Syringe Exchange(s); Red = No Syringe Exchange(s); Grey = No Information
Expanded Naloxone
Naloxone is a drug used to counteract the effects of opioid overdoses. Expanded Access refers to one of more of the following conditions: Naloxone purchase without a prescription; availability to schools, hospitals, and emergency response units for use in the event of an overdose.
States with Expanded Naloxone: AL, AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MO, MS, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Expanded Naloxone: None
Territories with Expanded Naloxone: Unknown
Figure 22. April 2022 Expanded Naloxone Coverage
Map Key: Purple = Expanded Naloxone; Red = Restricted Naloxone; Gray = No Information
Good Samaritan Laws
Good Samaritan Laws are laws that are designed to protect emergency services personnel, public or private employees, and/or citizens from being held legally liable for any negative healthcare outcomes as a result of providing "reasonable measures" of emergent care.
States with Samaritan Laws: AL, AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MO, MS, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Samaritan Laws: None
Territories with Samaritan Laws: Unknown
Figure 23. April 2022 Good Samaritan Laws Coverage
Map Key: Purple = Good Samaritan Laws; Red = No Good Samaritan Laws; Gray: No Information
Mandatory PDMP Reporting
Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs (PDMPs) are programs established by state and/or federal law that requires prescribing physicians and the fulfilling pharmacies to report to a state agency one or more of the following data points: Patient Names; Specific Drug(s) Prescribed; Prescription Dosage; Date; Time; Form of State-Issued ID.
States with PDMP Reporting: AL, AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without PDMP Reporting: MO, MT, SD
Territories with PDMP Reporting: Guam
Figure 24. April 2022 Mandatory Prescription Drug Monitoring Program Coverage
Map Key: Purple = Mandatory PDMP; Red = No Mandatory PDMP; Gray = No Information
Doctor Shopping Laws
Doctor Shopping Laws are those laws designed to prevent patients from seeking one or more of the same prescription from multiple doctors through the use of subterfuge, falsifying identity, or any other deceptive means. While federal law prohibits Doctor Shopping, most states also include provisions that prohibit patients from seeking a new prescription if another physician has denied a similar prescription within a certain period of time.
States with Doctor Shopping Laws: AL, AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MO, MS, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Doctor Shopping Laws: None
Territories with Doctor Shopping Laws: None
Figure 25. April 2022 Doctor Shopping Laws Coverage
Map Key: Purple = Doctor Shopping Laws; Red = No Doctor Shopping Laws; Grey = No Information
Physical Exam Required
Physical Exam Requirements are those that mandate that the prescribing physician perform a physical examination on a patient before providing a prescription for a controlled substance to determine if the prescription is medically necessary.
States with Physical Exam Required: AL, AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KY, LA, MD, MA, ME, MI, MN, MO, MS, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, PA, RI, SC, TN, TX, UT, VA, VT, WA, WV, WY, D.C.
States without Physical Exam Required: KS, MT, OR, SD, WI
Territories with Physical Exam Required: None
Figure 26. April 2022 Physical Exam Required Coverage
Map Key: Purple = Physical Exam Required; Red: No Physical Exam Required; Grey = No Information
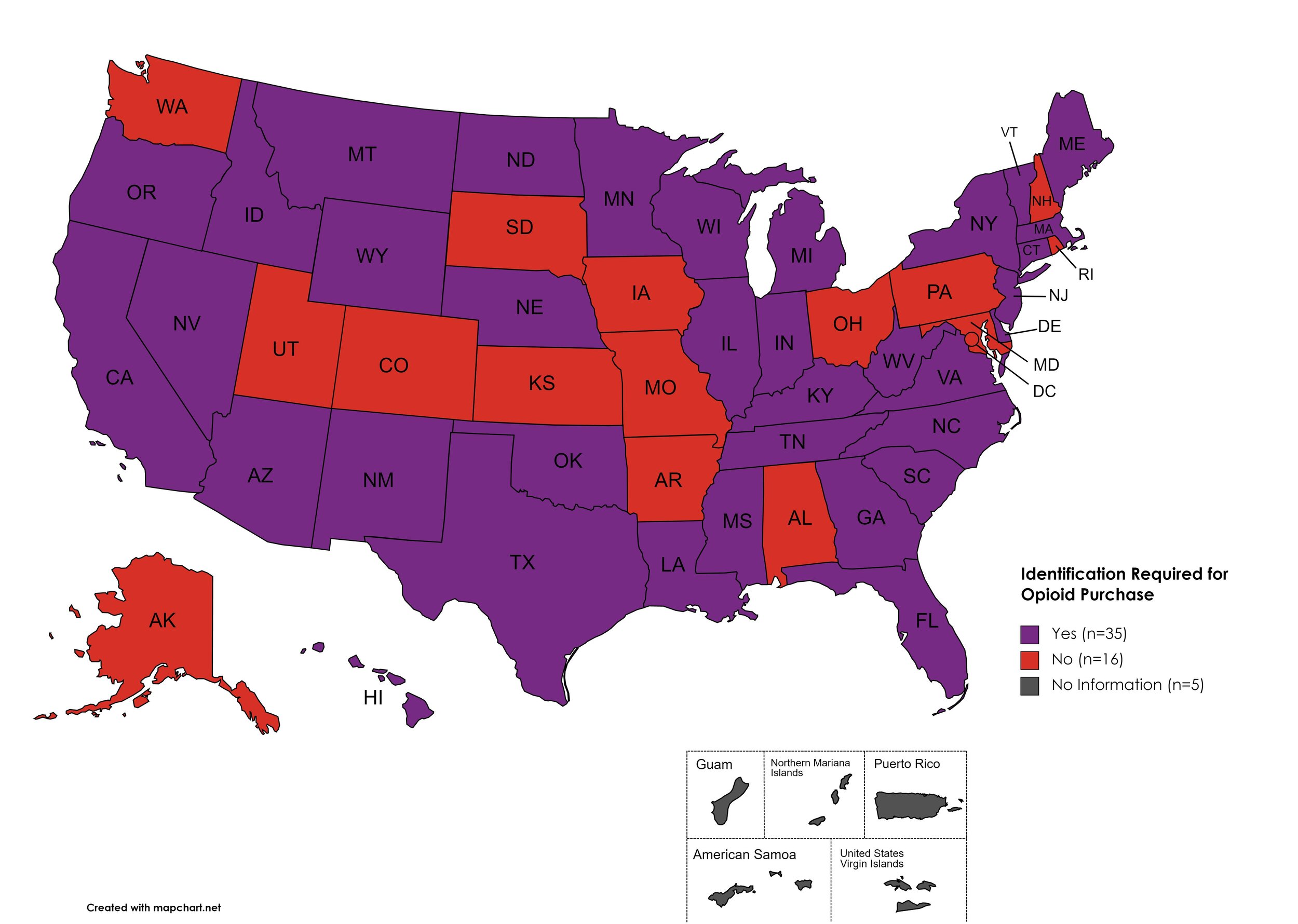
I.D. Required for Purchase of Opioid Prescription
Federal law requires anyone purchase a controlled substance to provide a state-issued identification (“I.D.”) in order to fill the prescription. Mandatory ID requirements go further and require that this information be recorded and stored in an effort to prevent the same patient from obtaining multiple or repeated prescriptions in a given period of time.
States with I.D. Required: AZ, CA, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, KY, LA, ME, MA, MI, MS, MN, MT, NE, NV, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OK, OR, SC, TN, TX, VT, VA, WV, WI, WY
States without I.D. Required: AL, AK, AR, CO, IA, KS, MD, MO, NH, OH, PA, RI, SD, UT, WA, D.C.
Territories with I.D. Required: Unknown
Figure 27. April 2022 I.D. Required Coverage
Map Key: Purple = I.D. Required; Red = No I.D. Required; Gray = No Information
Prescriber Education Required/Recommended
States that require/do not require that prescribing physicians undergo special training related to safer prescribing and utilization practices.
States with Prescriber Education Required: AL, AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, OH, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Prescriber Education Required: KS, MO, MT, ND, SD
Territories with Prescriber Education Required: Unknown
Figure 28. April 2022 Prescriber Education Required Coverage
Map Key: Purple = Prescriber Ed Required; Red = No Prescriber Ed Required; Gray = No Information
Medicaid Lock-In Program
Lock-In Programs are laws requiring that patients either receive prescriptions from only one physician and/or fill prescriptions from only one pharmacy.
States with Medicaid Lock-In Program: AL, AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, GA, ID, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MO, MS, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Medicaid Lock-In Program: FL, HI, SD
Territories with Medicaid Lock-In Program: Unknown
Figure 29. April 2022 Medicaid Lock-In Coverage
Map Key: Purple = Medicaid Lock-In; Red = No Medicaid Lock-In; Gray = No Information
April 2022 Notes:
In March of 2020, the DEA issued guidance regarding telehealth and physical exam requirements through the duration of the COVID-19 public health emergency, specifically with regard to physical exam requirements
Good Samaritan Laws may have a carve out for individuals illegally dispensing opioids or other illicit drugs
Doctor shopping laws in several states are found under "“fraud” statutes related to obtaining opioid prescriptions
Medicaid Pharmacy Lock-In Programs: Florida and Hawaii allow for but do not mandate Medicaid Pharmacy Lock-In by way of rule-making or waiver. Program activity is designated by Managed Care Organization
New Jersey has updated interpretation of existing state law to include mandatory PDMP reporting for certain controlled substances.
CANN is no longer able to independently verify the existence of an SSP in Kansas. KS state laws prohibit SSPs and syringes are included in the state’s drug paraphernalia law.
7. COVID-19 IMPACT ON HIV & HCV
The Community Access National Network’s blog began 2021 by assessing COVID-19’s impact on HIV, HCV, and Substance-Use Disorder. We've subsequently followed-up by asking, COVID-19: How Far We’ve Come & How Far We Have to Go? We continue to monitor developments in light of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic and its impacts on public health.
Additional Resources and Relevant Issues:
Declaration of Public Health Emergency Renewed - On April 12, 2022, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Secretary Xavier Becerra renewed the existing declaration of a public health emergency due to COVID-19. The previous declaration was set to expire on April 14th, 2022. To review some potential changes when the PHE ends, click here.
Lessons for COVID Found in US’s Lingering Fight Against HIV - NPR provides an enlightening look at the potential lessons in fighting COVID-19 by assessing where the United States stands in Ending the HIV Epidemic. Interviews with federal officials, patients, and advocates highlight existing disparities, why HIV remains prevalent despite effective treatments and a national public health program aimed at providing access to care for impoverished people living with HIV, and how a broader harm reduction approach (as opposed to treating patients as “unsavable”, meeting them where they’re at especially in situations of mistrust) might hold the keys to addressing both HIV and COVID-19.
The Impact of COVID-19 on HIV Testing, Treatment and Prevention in Louisiana - Louisiana is one of the several Southern states with some of the highest rates of new HIV diagnoses in the nation. Louisiana State University’s Olivia Landry reviews how the state has worked to combat HIV and how far the state slid when COVID-19 was declared a pandemic. Interviews with local providers and advocates focus on a massive reduction in testing, PrEP maintenance and uptake, and the effects of stigma plaguing the state as part of an evaluation as to where the state stands nearly two years into co-occurring pandemics.
HIV Treatments May Hold Key to Preventing COVID in PLWHA - HIV medications are making the COVID-19 news rounds again as a study in France sought to review the potential clinical benefits of particular therapies. The study found people living with HIV/AIDS (PLWHA) and being treated with protease inhibitors were less likely to develop COVID than their peers who were being treated with other therapies. Certain COVID treatments in development are also looking at the potential of protease inhibitors.
No, COVID Vaccines Do Not Increase Risks of Acquiring HIV-1 - In an open letter published in The Lancet, researchers respond to a faulty notion that certain COVID-19 vaccines using a particular adenovirus increase risks of acquiring HIV-1. The links included in the debunking effort cite existing research and even point toward using similar vectors in the development of potential HIV vaccines.
Willingness to Accept COVID Vaccination Among People Living with HIV in a High Prevalence Community - A small study evaluating the willingness of people living with HIV/AIDS (PLWHA) in South Africa found the majority of participants were willing to accept COVID-19 vaccinations. Willingness was associated with older age. However, a significant portion of participants still showed some hesitancy. Authors suggest public health messaging should target the reason for hesitancy in order to increase vaccination uptake among PLWHA. Disclaimer: pre-prints are not yet peer-reviewed.
Disasters Can Interrupt Access to Medications for the Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder - With a spike in overdose deaths occurring during the first years of the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers sought to assess how vulnerable communities lose access to medication assisted treatment during disasters, including hurricanes, tornadoes, flooding, and, yes, pandemics. Researchers found often community vulnerability is not matched with resources and access, leading to and exacerbating disparities.
She’s Been on the Front Line of Public Health Challenges. Nothing Prepared Her for COVID-19 - The Almanac provides a profile on Dr. Yvonne Maldonado, the founder of Stanford’s pediatric HIV clinic. Reflecting on her experience in tracking the original SARS outbreak, she quickly assessed COVID-19 would be more than an “outbreak” in January of 2020 and began having her students track the virus as part of the studies in epidemiology.
8. LATEST NEWS
Renewal of Determination That a Public Health Emergency Exists - On April 1, 2022, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Secretary Xavier Becerra renewed the ongoing declaration of public health emergency regarding the opioid crisis. The declaration is the latest in extensions regarding the opioid crisis, originating in October 2017.
White House Drug Control Strategy Stresses Harm reduction, Interdiction - On April 20, 2022, the Biden Administration released its inaugural National Drug Control Strategy. The strategy emphasizes harm reduction and addressing international supply chains for illegal and illicit substances. The strategy calls for expanding naloxone access, high quality medication assisted treatment and programs providing same, and improving data collection, especially among non-fatal overdoses.
Influential HIV Advocate, Rose Walton, Dies at Age 85 - Known for being both strong and kind, Rose Walton, for whom the the HIV Care Services Center at Stony Brook was named after, has passed. She is survived by her wife.
Tennessee Bill to Modernize HIV Criminalization Law Downsized - After receiving significant pushback for the scope of his proposed bill, Republican Bob Ramsey has limited his effort to modernizing Tennessee’s HIV criminalization law. The bill moving forward will now only remove the requirement for people convicted under the statute to register as sex offenders. His original bill would have allowed for certain affirmative defenses and reduced the penalty to a misdemeanor. He intends to introduce another measure next session in order to fully modernize the state’s law.
Illinois Poised to Take BIG Step in Ending the HIV Epidemic - A bill to allow pharmacists to dispense PrEP without the need for a doctor’s prescription has now passed the Illinois State’s House and Senate and is awaiting Governor Pritzker’s signature. The bill aligns with goals of President Biden’s budget and is backed by local HIV advocates.
The Need for Additional Funding in order to Achieve Elimination of Viral Hepatitis - The National Viral Hepatitis Roundtable (NVHR) has issued a statement in response to President Biden’s proposed FY 2023 budget. While the Biden budget proposal does increase hepatitis elimination funding, the increase is relatively modest compared to the funding advocates say is actually needed to eliminate viral hepatitis by 2030.
Colorado Grapples with Conflict between Harm Reduction Advocates and Law Enforcement - Harm reduction advocates and law enforcement officials clashed as the state considers a bill that would make distribution of fentanyl a felony. Law enforcement officials stated the measure “doesn’t go far enough” and are advocating for felony penalties for possession of the drug. Harm reduction advocates state increasing criminal penalties will only further harm the state’s efforts to combat a growing overdose crisis by discouraging public participation and trust in state-funded harm reduction programs and only exacerbate existing stigma.
Gilead’s Lawsuit Against Florida Network of Providers and Pharmacists Moves Forward - Gilead’s lawsuit from November 2020 against a network of clinics and pharmacies is finally moving forward after a judge has issued an asset freeze for the “ring leaders” of a scheme Gilead characterizes as intentionally abusing the manufacturer’s patient assistance program for PrEP, known as Advancing Access. Gilead has claimed the named defendants recruited homeless people and provided falsified information in order to receive free bottles of Truvada as PrEP and then resell them with mark up.
HIV Testing in PrEP Users Lower than Recommended - A European study evaluating the HIV and sexually transmitted infection (STI) testing rates of German PrEP users found many PrEP users were not necessarily getting tested as frequently as they should be. Previous experience with testing and the source of the person’s PrEP medication (formal and consistent, inconsistent, and informal sources for the medication) were strong predictors as to the user’s likelihood of regularly seeking screenings. Additionally, those who more regularly screened were also more likely to be diagnosed with an STI. Testing rates among participants was still higher than the estimated rate of testing among PrEP users in the United States.