Watch 01: January 2021
The HIV/HCV Co-Infection Watch is a project of the Community Access National Network (CANN) designed to research, monitor and report on HIV and Hepatitis C (HCV) co-infection in the United States. The January 2021 Watch includes timely updates herein. To read the project disclaimer and/or methodology, CLICK HERE.
1. FINDINGS
The following is a summary of the key findings for January 2021:
AIDS Drug Assistance Programs:
There are 56 State and Territorial AIDS Drug Assistance Programs (ADAPs) in the United States, 47 of which offer some form of coverage for Hepatitis C (HCV) treatment. Of those programs, 42 have expanded their HCV coverage to include the Direct-Acting Antiviral (DAA) regimens that serve as the current Standard of Care (SOC) for Hepatitis C treatment. Five (5) programs offer only Basic Coverage and 9 programs offer No Coverage. Three (3) territories – American Samoa, Marshall Islands, and Northern Mariana Islands – are not accounted for in this data. A state-by-state Drug Formulary breakdown of coverage is included in the January 2021 Updates, with accompanying drug-specific maps in Figures 1 – 10.
Medicaid Programs:
There are 59 State and Territorial Medicaid programs in the United States, and data is represented for all fifty states and the District of Columbia. As of October 01, 2016, all 50 states and the District of Columbia offer Expanded Coverage. A state-by-state PDL breakdown of coverage is included in the January 2021 Updates, with accompanying drug-specific maps in Figures 11 – 20.
Harm Reduction Programs:
Every State and Territory in the United States currently provides funding for low-income people living with substance abuse issues to enter state-funded rehabilitation services (National Center for Biotechnology Information, n.d.). Forty-seven (47) States and Territories currently have Syringe Services Programs (SSPs) in place, regardless of the legality. Fifty (50) states and the District of Columbia have expanded access to Naloxone to avert opioid drug overdoses. Fifty (50) states and the District of Columbia have Good Samaritan laws or statutes that provide some level of protection for those rendering emergency services during drug overdoses. Thirty-eight (38) states make reporting to Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs (PDMPs) mandatory, requiring physicians and/or pharmacists to report prescriptions written or filled to a state agency for monitoring. Forty (40) states have Opioid-Specific Doctor Shopping Laws preventing patients from attempting to receive multiple prescriptions from numerous physicians, and/or from withholding information in order to receive prescriptions. Forty (40) states mandate a Physical Exam Requirement in order for patients to receive a prescription for opioid drugs. Twenty-seven (27) states have in place an ID Requirement mandating that people filling opioid prescriptions present a state-issued ID prior to receiving their prescription. Forty-five (45) states require prescribing physicians to attend mandatory and continuing opioid prescribing education sessions. Forty-four (44) states have Medicaid doctor/pharmacy Lock-In programs that require patients to receive prescriptions from a single physician and/or fill prescriptions from a single pharmacy. A state-by-state program breakdown is included in the January 2021 Updates, with accompanying drug-specific maps in Figures 21-29.
2. AIDS DRUG ASSISTANCE PROGRAMS (ADAPs) & HCV THERAPIES
Of the 56 respective State and Territorial ADAPs, only 9 (ID, KS, KY, OH, UT, VT, GU, PW, VI) do not offer any coverage for HCV drug therapies. States whose formularies are not available on the state-run website have been checked against the most recent National Alliance of State and Territorial AIDS Directors (NASTAD) formulary database (last updated April 16, 2020). The data presented are current as of January 15, 2021.
January 2021 Updates:
Basic Coverage
States with Basic HCV Medications Coverage: AL, AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, IL, IN, IA, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, MO, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, SD, TN, TX, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Basic HCV Medications Coverage: ID, KS, KY, OH, UT, VT
Territories with Basic HCV Medications Coverage: P.R.
Figure 1. January 2021 ADAP Coverage - Basic HCV Medications
Map Key: Yellow = Basic HCV Medication Coverage; Red = No Basic HCV Medication Coverage/No Information regarding Basic HCV Medication Coverage
Sovaldi
States with Sovaldi Coverage: AZ, CA, CO, GA, HI, IL, IN, IA, LA, ME, MD, MA, MN, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, ND, OK, OR, PA, SD, TX, VA, WA, WY, D.C.
States without Sovaldi Coverage: AL, AK, AR, CT, DE, FL, ID, KS, KY, MI, MS, MO, MT, NY, NC, OH, RI, SC, TN, UT, VT, WV, WI
Territories with Sovaldi Coverage: P.R.
Figure 2. January 2021 ADAP Coverage - Sovaldi
Map Key: Yellow = Sovaldi Coverage; Red = No Sovaldi Coverage/No Information regarding Sovaldi Coverage
Harvoni
States with Harvoni Coverage: AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, IL, IN, IA, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NC, ND, OK, OR, PA, SD, TN, TX, VA, WA, WY, D.C.
States without Harvoni Coverage: AL, AK, ID, KS, KY, MO, MT, NY, OH, RI, SC, UT, VT, WV, WI
Territories with Harvoni Coverage: P.R.
Figure 3. January 2021 ADAP Coverage - Harvoni
Map Key: Yellow = Harvoni Coverage; Red = No Harvoni Coverage/No Information regarding Harvoni Coverage
Zepatier
States with Zepatier Coverage: AL, AZ, AR, CA, CO, FL, GA, HI, IL, IA, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OR, PA, SD, TX, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Zepatier Coverage: AK, CT, DE, ID, IN, KS, KY, MO, MT, OH, OK, RI, SC, UT, VT
Territories with Zepatier Coverage: P.R.
Figure 4. January 2021 ADAP Coverage - Zepatier
Map Key: Yellow = Zepatier Coverage; Red = No Zepatier Coverage/No Information regarding Zepatier Coverage
Epclusa
States with Epclusa Coverage: AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, GA, HI, IL, IN, IA, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, MO, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, ND, OR, PA, SD, TN, TX, VA, WA, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Epclusa Coverage: AL, AK, DE, FL, ID, KS, KY, MT, NY, NC, OH, OK, RI, SC, UT, VT, WV
Territories with Epclusa Coverage: P.R.
Figure 5. January 2021 ADAP Coverage - Epclusa
Map Key: Yellow = Epclusa Coverage; Red = No Epclusa Coverage/No Information regarding Epclusa Coverage
Vosevi
States with Vosevi Coverage: CA, CT, HI, IL, IN, IA, LA, MD, MA, MN, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, ND, OR, SD, TN, TX, WA, WY, D.C.
States without Vosevi Coverage: AL, AK, AZ, AR, CO, DE, FL, GA, ID, KS, KY, ME, MI, MS, MO, MT, NY, NC, OH, OK, PA, RI, SC, UT, VT, VA, WV, WI
Territories with Vosevi Coverage: P.R.
Figure 6. January 2021 ADAP Coverage - Vosevi
Map Key: Yellow = Vosevi Coverage; Red = No Vosevi Coverage/No Information regarding Epclusa Coverage
Mavyret
States with Mavyret Coverage: AL, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, FL, GA, HI, IL, IN, IA, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, MO, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OK, OR, PA, SD, TN, TX, VA, WA, WV, WY, D.C.
States without Mavyret Coverage: AK, DE, ID, KS, KY, OH, RI, SC, UT, VT, WI
Territories with Mavyret Coverage: P.R.
Figure 7. January 2021 ADAP Coverage - Mavyret
Map Key: Yellow = Mavyret Coverage; Red = No Mavyret Coverage/No Information regarding Mavyret Coverage
Pegasys
States with Pegasys Coverage: AL, CA, CO, CT, DE, HI, IL, IA, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NC, ND, OR, PA, RI, SD, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Pegasys Coverage: AK, AZ, AR, FL, GA, ID, IN, KS, KY, MS, MO, MT, NY, OH, OK, SC, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA
Territories with Pegasys Coverage: None/Unknown
Figure 8. January 2021 ADAP Coverage - Pegasys
Map Key: Yellow = Pegasys Coverage; Red = No Pegasys Coverage/No Information regarding Pegasys Coverage
Harvoni (generic)
States with Harvoni (generic) Coverage: AZ, AR, CA, CT, FL, HI, IL, IA, ME, MD, MA, MN, MS, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NC, ND, OK, OR, PA, SD, TN, WA, WY, D.C.
States without Harvoni (generic)Coverage: AL, AK, DE, ID, KS, KY, LA, OH, RI, SC, UT, VT, WI
Territories with Harvoni (generic) Coverage: P.R.
Figure 9. January 2021 ADAP Coverage - Harvoni (Generic)
Map Key: Yellow = Harvoni (Generic) Coverage; Red = No Harvoni (Generic) Coverage/No Information regarding Harvoni (Generic) Coverage
Epclusa (generic)
States with Epclusa (generic) Coverage: AZ, AR, CA, CT, HI, IL, IA, ME, MD, MA, MN, MS, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NC, ND, OR, PA, SD, TN, WA, WY, D.C.
States without Epclusa (generic) Coverage: AL, AK, CO, DE, FL, GA, ID, IN, KS, KY, LA, MI, MO, MT, NY, OH, OK, RI, SC, TX, UT, VT, VA, WV, WI
Territories with Epclusa (generic) Coverage: P.R.
Figure 10. January 2021 ADAP Coverage - Epclusa (generic)
Map Key: Yellow = Epclusa (generic) Coverage; Red = No Epclusa (generic) Coverage/No Information regarding Epclusa (generic) Coverage
January 2021 Notes:
States with Open Formularies: IL, IA, MA, MN, NE, NH, NJ, NM, ND, OH, OR, WA, WY
N.B. – Although Ohio is listed by NASTAD as having an open formulary, both NASTAD’s ADAP Formulary Database and Ohio’s ADAP website indicates that the state does not offer any treatment for HCV
N.B. – Although North Dakota has adopted an open formulary, they provide only co-pay and deductible assistance for HCV medications
N.B. – Wyoming's ADAP Open Formulary document, the following disclaimer related to HCV is made: Hepatitis C treatment medications (i.e. Harvoni, Sovaldi, Ribavirin, Zepatier, Epclusa) must be prior authorized. To be eligible, clients must have applied for prior authorization from their insurance plan and the WY ADAP Hepatitis C Treatment checklist must be completed and signed by the provider and client
Colorado’s ADAP offers five coverage options – Standard ADAP, HIV Medical Assistance Program (HMAP), Bridging the Gap Colorado (BTGC), HIV Insurance Assistance Program (HIAP), and Supplemental Wrap Around Program (SWAP). ‘Yes’ indications in Figure 1. for Colorado denote that at least one of these programs offers coverage for each respective drug. The Standard ADAP Formulary covers medications only if funds are available to do so.
Louisiana’s ADAP (Louisiana Health Access Program – LA HAP) offers two coverage options – Uninsured (Louisiana Drug Assistance Program – L-DAP) and Insured (Health Insurance Program – HIP). HIP pays for the cost of treatment only if the client’s primary insurance covers the drug under its formulary.
3. MEDICAID PROGRAMS & HCV THERAPIES
All 50 states and the District of Columbia continue to offer some form of HCV coverage. All 50 states and the District of Columbia have expanded their Preferred Drug Lists to include at least one HCV Direct Acting Agent (DAA).
January 2021 Updates:
Basic Coverage
States with Basic HCV Medications Coverage: AL, AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MO, MS, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Basic HCV Medications Coverage: None
Figure 11. January 2021 Medicaid Coverage - Basic HCV Medications
Map Key: Blue = Basic HCV Medication Coverage; Yellow = No Basic HCV Medication Coverage/No Information regarding Basic HCV Medication Coverage
Sovaldi
States with Sovaldi Coverage: AK, AR, CA, CO, DE, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MO, MS, MT, NE, NV, NH, NY, NC, ND, OH, PA, RI, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Sovaldi Coverage: AL, AZ, CT, FL, NJ, NM, OR, SC
Figure 12. January 2021 Medicaid Coverage - Sovaldi
Map Key: Blue = Sovaldi Coverage; Yellow = No Sovaldi Coverage/No Information regarding Sovaldi Coverage
Harvoni
States with Harvoni Coverage: AL, AK, AR, CA, CO, DE, GA, HI, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MO, MS, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NY, NC, ND, OK, PA, RI, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Harvoni Coverage: AZ, CT, FL, ID, NM, OH, OR, SC
Figure 13. January 2021 Medicaid Coverage - Harvoni
Map Key: Blue = Harvoni Coverage; Yellow = No Harvoni Coverage/No Information regarding Harvoni Coverage
Zepatier
States with Zepatier Coverage: AL, AK, CA, CO, DE, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MO, MS, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NY, NC, ND, OH, OR, PA, RI, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Zepatier Coverage: AZ, CT, FL, NM, OK, OR, SC
Figure 14. January 2021 Medicaid Coverage - Zepatier
Map Key: Blue = Zepatier Coverage; Yellow = No Zepatier Coverage/No Information regarding Zepatier Coverage
Epclusa
States with Epclusa Coverage: AL, AK, AR, CA, CO, CT, GA, HI, IL, IN, KS, KY, LA, ME, MA, MI, MN, MO, MS, MT, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OK, OR, PA, RI, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Epclusa Coverage: AZ, DE, FL, ID, IA, MD, NE, OH, SC
Figure 15. January 2021 Medicaid Coverage - Epclusa
Map Key: Blue = Epclusa Coverage; Yellow = No Epclusa Coverage/No Information regarding Epclusa Coverage
Vosevi
States with Vosevi Coverage: AK, AR, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, KS, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MO, MS, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, PA, RI, SC, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Vosevi Coverage: AL, AZ, CA, IA, NM, NE, OK, OR
Figure 16. January 2021 Medicaid Coverage - Vosevi
Map Key: Blue = Vosevi Coverage; Yellow = No Vosevi Coverage/No Information regarding Vosevi Coverage
Mavyret
States with Mavyret Coverage: AL, AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MO, MS, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OR, PA, RI, SC, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Mavyret Coverage: OK
Figure 17. January 2021 Medicaid Coverage - Mavyret
Map Key: Blue = Mavyret Coverage; Yellow = No Mavyret Coverage/No Information regarding Mavyret Coverage
Pegasys
States with Pegasys Coverage: AK, AZ, CA, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NY, NC, OH, OR, PA, RI, SD, TN, TX, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, D.C.
States without Pegasys Coverage: AL, AR, CO, KS, MO, NM, ND, OK, SC, UT, WY
Figure 18. January 2021 Medicaid Coverage - Pegasys
Map Key: Blue = Pegasys Coverage; Yellow = No Pegasys Coverage/No Information regarding Pegasys Coverage
Harvoni (generic)
States with Harvoni (generic) Coverage: AL, AK, CA, CO, DE, HI, IL, IN, IA, KY, LA, MD, MA, MI, MN, MO, MS, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, PA, RI, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, D.C.
States without Harvoni (generic) Coverage: AZ, AR, CT, FL, GA, ID, KS, ME, NM, OR, SC, WY
Figure 19. January 2021 Medicaid Coverage - Harvoni (generic)
Map Key: Blue = Harvoni (generic) Coverage; Yellow = No Harvoni (generic) Coverage/No Information regarding Harvoni (generic) Coverage
Epclusa (generic)
States with Epclusa (generic) Coverage: AL, AK, AZ, CA, CO, DE, FL, HI, IL, IN, KY, LA, MD, MA, MI, MN, MO, MS, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, D.C.
States without Epclusa (generic) Coverage: AR, CT, GA, ID, IA, KS, ME,WY
Figure 20. January 2021 Medicaid Coverage - Epclusa (generic)
Map Key: Blue = Epclusa (generic) Coverage; Yellow = No Epclusa (generic) Coverage/No Information regarding Epclusa (generic) Coverage
January 2021 Notes:
The follow states’ Medicaid programs offer multiple coverage plans for their respective Medicaid clients. The plan highlighted in bold typeface represents the most comprehensive plan with the most drugs covered in the respective state:
Hawaii – (1.) Advantage Plus; (2.) QUEST Integration
New Jersey – (1.) Aetna; (2.) AmeriGroup NJ; (3.) Horizon NJ Health; (4.) UnitedHealthcare of New Jersey; (5.) WellCare
New Mexico – (1.) BlueCross BlueShield of New Mexico; (2.) Presbyterian Centennial Care; (3) Western Sky Community Care
Kentucky has adopted a Unified Medicaid Formulary
Louisiana has a Unified Medicaid Formulary
Ohio – Ohio has a Unified Medicaid Formulary that applies to all MCOs
No data is has been made available by the Medicaid programs in the U.S. Territories
*Medicaid coverage excludes patients from most drug manufacturer patient assistance programs (PAPs)
4. VETERANS PROGRAMS & HCV THERAPIES
The Veteran's Administration (VA) currently offers coverage for all HCV drugs. This is according to the most recent VA National Formulary, dated July 2018 (U.S. Dept. of V.A., 2018a). The VA Treatment Considerations and Choice of Regimen for HCV-Mono-Infected and HIV/HCV Co-Infected Patients (U.S. Dept. of V.A., 2018b) lists the following therapies as preferred treatments:
Abbreviations:
- CTP – Child-Turcotte-Pugh (score used to assess severity of cirrhosis)
- IU/mL – International Units Per Milliliter
- PEG-IFN/IFN – Peginterferon/Interferon
- RAS – Resistance-associated substitutions
- RBV – Ribavirin
Genotype 1:
Treatment-naïve without or with cirrhosis (CTP A):
Zepatier: 1 tablet orally daily for 12 weeks if GT1a without baseline NS5A RAS or GT1b
Mavyret: 3 tablets orally daily with food
If non-cirrhotic: 8 weeks
If cirrhotic: 12 weeks
Harvoni: 1 tablet orally daily
If HCV-monoinfected, non-cirrhotic, and baseline HCV RNA <6 million IU/mL: 8 weeks
If cirrhotic, baseline HCV RNA ≥6 million IU/mL or HIV/HCV coinfected: 12 weeks
Consider adding RBV in cirrhotic patients
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily for 12 weeks
Treatment-naïve with decompensated cirrhosis (CTP B or C):
Harvoni: 1 tablet orally daily + RBV (600 mg/day and increase by 200 mg/day every 2 weeks only as tolerated) for 12 weeks
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily + RBVd for 12 weeks; start at lower RBV doses as clinically indicated (e.g., baseline Hgb).
Treatment-experienced (NS5A- and SOF-naïve [e.g., failed PEG-IFN/RBV ± NS3/4A PI]) without or with cirrhosis (CTP A)
Zepatier: 1 tablet orally daily for 12 weeks if GT1b, or if failed only PEG-IFN/RBV and GT1a without baseline NS5A RAS
Mavyret: 3 tablets orally daily with food
If PEG-IFN/RBV-experienced: 8 weeks if non-cirrhotic or 12 weeks if cirrhotic
If NS3/4A PI + PEG-IFN/RBV-experienced: 12 weeks
Harvoni: 1 tablet orally daily for 12 weeks; add RBVd if cirrhotic
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily for 12 weeks
Treatment-experienced (NS5A-naïve and SOF-experienced) without or with cirrhosis (CTP A)
Mavyret: 3 tablets orally daily with food
If PEG-IFN/RBV + Sovaldi-experienced: 8 weeks if non-cirrhotic or 12 weeks if cirrhotic
If Olysio + Sovaldi-experienced: 12 weeks
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily for 12 weeks if GT1b
Treatment-experienced (prior NS5A-containing regimen) without or with cirrhosis (CTP A)
Mavyret: 3 tablets orally daily with food for 16 weeks if failed only an NS5A inhibitor without NS3/4A PI (e.g., Harvoni)
Vosevi: 1 tablet orally daily with food for 12 weeks
Treatment-experienced with decompensated cirrhosis (CTP B or C)
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily + RBV; start at lower RBV doses as clinically indicated (e.g., baseline Hgb);
If NS5A-naïve: 12 weeks
If NS5A-experienced: 24 weeks; NOT FDA approved for 24 weeks
Genotype 2:
Treatment-naïve or treatment-experienced (PEG-IFN/IFN ± RBV or Sovaldi + RBV ± PEG-IFN) without or with cirrhosis (CTP A)
Mavyret: 3 tablets orally daily with food
If non-cirrhotic: 8 weeks
If cirrhotic: 12 weeks
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily for 12 weeks
Treatment-experienced (NS5A-experienced) without or with cirrhosis (CTP A)
Vosevi: 1 tablet orally daily with food for 12 weeks
Treatment-naïve or treatment-experienced patients with decompensated cirrhosis (CTP B or CTP C)
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily + RBV; start at lower RBV doses as clinically indicated (e.g., baseline Hgb)
If NS5A-naïve: 12 weeks
If NS5A-experienced: 24 weeks
Genotype 3:
Treatment-naïve without cirrhosis or with cirrhosis (CTP A)
Mavyret: 3 tablets orally daily with food for 12 weeks
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily for 12 weeks
If CTP A, test for NS5A RAS
Add RBV if Y93H RAS present
Treatment-experienced (PEG-IFN ± RBV or Sovaldi + RBV ± PEG-IFN) without or with cirrhosis (CTP A)
Mavyret: 3 tablets orally daily with food for 16 weeks
Treatment-experienced (NS5A-experienced) without or with cirrhosis (CTP A)
Vosevi: 1 tablet orally daily with food for 12 weeks
If CTP A, consider adding RBV (no supporting data)
Treatment-naïve or treatment-experienced with decompensated cirrhosis (CTP B or CTP C)
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily + RBV; start at lower RBV doses as clinically indicated (e.g., baseline Hgb)
If NS5A-naïve: 12 weeks
If NS5A-experienced: 24 weeks
Genotype 4:
Treatment-naïve without or with cirrhosis (CTP A)
Zepatier: 1 tablet orally daily for 12 weeks
Mavyret: 3 tablets orally daily with food
If non-cirrhotic: 8 weeks
If cirrhotic: 12 weeks
Harvoni: 1 tablet orally daily for 12 weeks
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily for 12 weeks
Treatment-naïve with decompensated cirrhosis (CTP B or C)
Harvoni: 1 tablet orally daily + RBV (600 mg/day and increase by 200 mg/day every 2 weeks only as tolerated) for 12 weeks
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily + RBV for 12 weeks; start at lower RBV doses as clinically indicated (e.g., baseline Hgb)
Treatment-experienced (Sovaldi-experienced and NS5A-naïve) without or with cirrhosis (CTP A)
Mavyret: 3 tablets orally daily with food for 12 weeks
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily + RBV for 12 weeks; start at lower RBV doses as clinically indicated (e.g., baseline Hgb)
Treatment-experienced (NS5A-experienced) without or with cirrhosis (CTP A)
Vosevi: 1 tablet orally daily with food for 12 weeks
Treatment-experienced with decompensated cirrhosis (CTP B or CTP C)
Epclusa: 1 tablet orally daily + RBV; start at lower RBV doses as clinically indicated (e.g., baseline Hgb)
If NS5A-naïve: 12 weeks
If NS5A-experienced: 24 weeks; NOT FDA approved for 24 weeks
5. PATIENT ASSISTANCE PROGRAMS
The drug manufacturers and various national nonprofit organizations offer a variation of patient assistance programs (PAPs) to assist patients in accessing treatments. They include:
Support Path (Gilead Sciences):
Financial Assistance
Provides Co-Pay Coupons for Sovaldi, Harvoni, Harvoni (Generic), Epclusa, Epclusa (Generic), and Vosevi
Co-Pay Coupons cover out-of-pocket costs up to 25% of the catalog price of a 12-week regimen (3 bottles/packages) of Sovaldi, Harvoni, Harvoni (Generic), Epclusa, Epclusa (Generic), or Vosevi
Excludes patients enrolled in Medicare Part D or Medicaid
Insurance Support
Researches and verifies patient’s benefits, and gives information they need about coverage options and policies
Explain Prior Authorization process and works with HCV Specialist’s office so they can submit PA forms to a patient’s insurance company
May be able to provide assistance with appeals process
Website: http://www.mysupportpath.com/
AbbVie Mavyret Co-Pay Savings Card:
Financial Assistance
Patient may be eligible to pay as little as $5
Excludes patients enrolled in Medicare Part D, Medicare Advantage, Medigap, Medicaid, TRICARE, Department of Defense, or Veterans Affairs programs)
NeedyMeds:
NeedyMeds Drug Discount Card
Designed to lower cost of prescription medications by up to 80% at participating pharmacies
NeedyMeds DOES NOT keep a list of prescription medications covered
No eligibility requirements
Patients CANNOT be enrolled in any insurance
CANNOT be used in combination with government healthcare programs, but CAN be used IN PLACE of program
CANNOT be combined with other offers
Website: http://ow.ly/fEJo309cJ7Z
The Assistance Fund:
Status: WAITLISTED
Requires provider referral
Copay assistance
Eligibility Criteria:
US citizen or permanent resident
Diagnosed with the disease for which you are applying
Prescribed an FDA-approved treatment for the disease
Have prescription coverage for the prescribed treatment
Meet financial eligibility criteria based upon household income and size
Patient Advocate Foundation Co-Pay Relief:
Status: CLOSED
Maximum award of $15,000
Eligibility Requirements:
Patient must be insured, and insurance must cover prescribed medication
Confirmed HCV diagnosis
Reside and receive treatment in the U.S.
Income falls below 400% of FPL with consideration of the Cost of Living Index (COLI) and the number in the household
Patient Access Network (PAN) Foundation:
Status: OPEN
Co-Pay Assistance with a maximum award of $6,000
Patients may apply for a second grant during their eligibility period subject to availability of funding
Eligibility Requirements:
Must be being treated for HCV
Have insurance that covers HCV prescribed medication
Medication must be listed on PAN’s list of covered medications: https://www.panfoundation.org/index.php/en/patients/medications-covered
Income falls below 500% of FPL
Residing and receiving treatment in the U.S. (citizenship NOT required)
Website: https://www.panfoundation.org/index.php/en/patients/assistance-programs/hepatitis-c
HealthWell Foundation:
Status: OPEN
Co-Pay Assistance with a maximum award of $30,000
Minimum Co-Pay Reimbursement Amount: None
Minimum Premium Reimbursement Amount: None
Eligibility Requirements:
Must be being treated for HCV
Have insurance that covers HCV prescribed medication
Income falls below 500% of FPL
Receiving treatment in the U.S.
Website: https://www.healthwellfoundation.org/fund/hepatitis-c/
6. HARM REDUCTION PROGRAMS
Harm Reduction, as it relates to opioid abuse and HCV, are measures designed to serve as preventive or monitoring efforts in combating opioid prescription drug and heroin abuse, and as an effect, helping to prevent the spread of HCV and HIV. The Co-Infection Watch covers the following measures: Syringe Exchange, Expanded Naloxone Access, Good Samaritan Laws, Mandatory PDMP Reporting, Doctor Shopping Laws, Physical Exam Requirements, ID Requirements for Purchase, Required or Recommended Prescriber Education, and Lock-In Programs (Editor’s Note: Program descriptions provided herein).
January 2021 Updates:
Syringe Exchange
Syringe Services Programs (SSPs) exist to provide injection drug users (or those whose prescriptions require injection) with clean syringes and/or in exchange for used ones. (N.b. – states listed as "Y" indicate only that a Syringe Services Program (SSP) exists within the state, regardless of the legality of SSPs under state law).
States with Syringe Exchange: AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MO, MT, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, D.C.
States without Syringe Exchange: AL, MS, NE, SD, WY
Territories with Syringe Exchange: Puerto Rico, U.S. Virgin Islands
Figure 21. January 2021 Syringe Exchange Coverage
Map Key: Purple = Syringe Exchange(s); Red = No Syringe Exchange(s); Grey = No Information
Expanded Naloxone
Naloxone is a drug used to counteract the effects of opioid overdoses. Expanded Access refers to one of more of the following conditions: Naloxone purchase without a prescription; availability to schools, hospitals, and emergency response units for use in the event of an overdose.
States with Expanded Naloxone: AL, AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MO, MS, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Expanded Naloxone: None
Territories with Expanded Naloxone: Unknown
Figure 22. January 2021 Expanded Naloxone Coverage
Map Key: Purple = Expanded Naloxone; Red = Restricted Naloxone; Gray = No Information
Good Samaritan Laws
Good Samaritan Laws are laws that are designed to protect emergency services personnel, public or private employees, and/or citizens from being held legally liable for any negative healthcare outcomes as a result of providing "reasonable measures" of emergent care.
States with Samaritan Laws: AL, AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MO, MS, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Samaritan Laws: None
Territories with Samaritan Laws: Unknown
Figure 23. January 2021 Good Samaritan Laws Coverage
Map Key: Purple = Good Samaritan Laws; Red = No Good Samaritan Laws; Gray: No Information
Mandatory PDMP Reporting
Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs (PDMPs) are programs established by state and/or federal law that requires prescribing physicians and the fulfilling pharmacies to report to a state agency one or more of the following data points: Patient Names; Specific Drug(s) Prescribed; Prescription Dosage; Date; Time; Form of State-Issued ID.
States with PDMP Reporting: AK, AZ, AR, CA, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, IL, IN, IA, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, NE, NV, NH, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, TN, UT, VT, VA, WV, WI
States without PDMP Reporting: AL, CO, ID, KS, MN, MS, MO, MT, NJ, SD, TX, WA, WY, D.C.
Territories with PDMP Reporting: Guam
Figure 24. January 2021 Mandatory Prescription Drug Monitoring Program Coverage
Map Key: Purple = Mandatory PDMP; Red = No Mandatory PDMP; Gray = No Information
Doctor Shopping Laws
Doctor Shopping Laws are those laws designed to prevent patients from seeking one or more of the same prescription from multiple doctors through the use of subterfuge, falsifying identity, or any other deceptive means. Some states also include provisions that prohibit patients from seeking a new prescription if another physician has denied a similar prescription within a certain period of time.
States with Doctor Shopping Laws: AL, AK, AZ, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, IL, IN, IA, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MS, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, PA, SC, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, WV, WI, WY
States without Doctor Shopping Laws: AR, ID, KS, MN, MO, NM, OR, RI, VA, WA, D.C.
Territories with Doctor Shopping Laws: None
Figure 25. January 2021 Doctor Shopping Laws Coverage
Map Key: Purple = Doctor Shopping Laws; Red = No Doctor Shopping Laws; Grey = No Information
Physical Exam Required
Physical Exam Requirements are those that mandate that the prescribing physician perform a physical examination on a patient before providing a prescription for a controlled substance to determine if the prescription is medically necessary.
States with Physical Exam Required: AL, AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KY, LA, ME, MN, MO, MS, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NC, ND, OH, OK, PA, RI, SC, TN, TX, UT, VA, WA, WV, D.C.
States without Physical Exam Required: KS, MD, MA, MI, MT, NY, OR, SD, VT, WI, WY
Territories with Physical Exam Required: None
Figure 26. January 2021 Physical Exam Required Coverage
Map Key: Purple = Physical Exam Required; Red: No Physical Exam Required; Grey = No Information
I.D. Required for Purchase of Opioid Prescription
Federal law requires anyone purchase a controlled substance to provide a state-issued identification (“I.D.”) in order to fill the prescription. Mandatory ID requirements go further and require that this information be recorded and stored in an effort to prevent the same patient from obtaining multiple or repeated prescriptions in a given period of time.
States with I.D. Required: CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, LA, ME, MA, MI, MN, MT, NV, NM, NY, NC, ND, OK, OR, SC, TX, VT, VA, WV, WI
States without I.D. Required: AL, AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, IA, KS, KY, MD, MS, MO, NE, NH, NJ, OH, PA, RI, SD, TN, UT, WA, WY, D.C.
Territories with I.D. Required: Unknown
Figure 27. January 2021 I.D. Required Coverage
Map Key: Purple = I.D. Required; Red = No I.D. Required; Gray = No Information
Prescriber Education Required/Recommended
States that require/do not require that prescribing physicians undergo special training related to safer prescribing and utilization practices.
States with Prescriber Education Required: AL, AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, OH, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, TN, TX, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, D.C.
States without Prescriber Education Required: KS, MO, MT, ND, SD, WY
Territories with Prescriber Education Required: Unknown
Figure 28. January 2021 Prescriber Education Required Coverage
Map Key: Purple = Prescriber Ed Required; Red = No Prescriber Ed Required; Gray = No Information
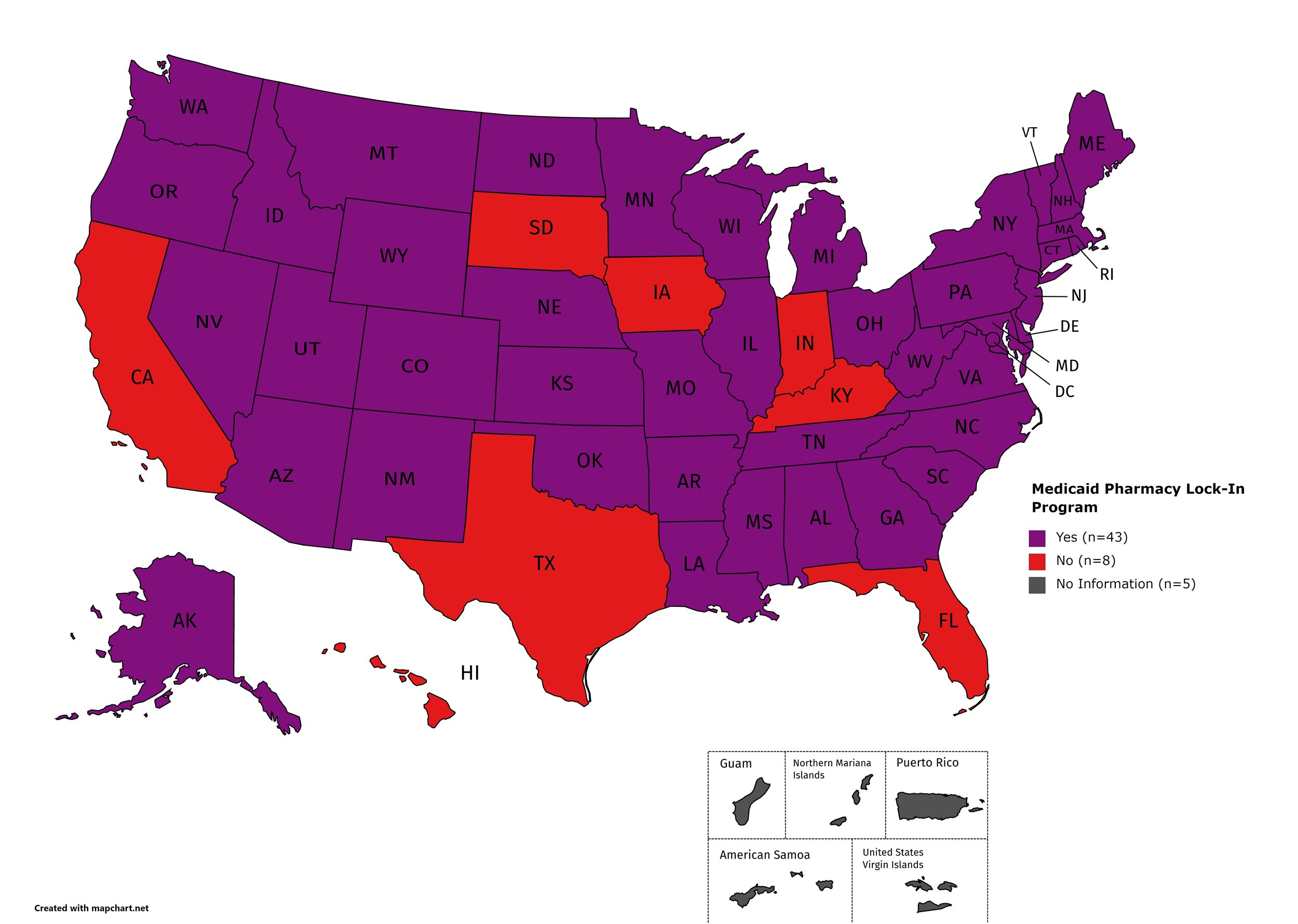
Medicaid Lock-In Program
Lock-In Programs are laws requiring that patients either receive prescriptions from only one physician and/or fill prescriptions from only one pharmacy.
States with Medicaid Lock-In Program: AL, AK, AZ, AR, CO, CT, DE, GA, ID, IL, KS, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MO, MS, MT, NE, NV, NH, NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, TN, UT, VT, VA, WA, WV, WI, WY, D.C.
States without Medicaid Lock-In Program: CA, FL, HI, IN, IA, KY, SD, TX
Territories with Medicaid Lock-In Program: Unknown
Figure 29. January 2021 Medicaid Lock-In Coverage
Map Key: Purple = Medicaid Lock-In; Red = No Medicaid Lock-In; Gray = No Information
January 2021 Notes:
No notes.
7. COVID-19 IMPACT ON HIV & HCV
The Community Access National Network’s blog began 2021 assessing COVID-19’s impact on HIV, HCV, and Substance-Use Disorder.
Additional Resources and Relevant Issues:
Kaiser Family Foundation conducted a national survey of COVID-19 impacts among Ryan White service providers
COVID-19 has emphasized the need public health programs, officials, and funders to consider housing as a critical intervention tool in controlling infectious diseases and as a socio-economic determinant of health. A recent study highlighted how evictions contributed to additional, preventable COVID-19 transmissions.
At least 181 state and local public health officials have resigned, been fired, or retired since March 2020 - often associated with public backlash and politicizing of COVID-19 responses. Many of these officials’ work includes HIV & HCV planning and implementation on state levels, leaving a question as to how this will impact the future of HIV & HCV programs.
COVID-19 has shone a light on professional ethical considerations of individual and systemic interventions. How this idea may be considered with regard to program and intervention designs HIV, HCV, and Substance-Use disorder should be closely watched.
8. LATEST NEWS
Health and Human Services publishes Viral Hepatitis National Strategic Plan for the United States: A Roadmap to Elimination (2021-2025).
Health and Human Services publishes HIV National Strategic Plan (2021-2025).
Health and Human Services publishes first STI National Strategic Plan (2021-2025).
Health and Human Services “X’es” the X Waiver, allowing more providers to prescribe buprnorphine without additional certification, and adding a tool to the fight the Opioid Epidemic.
Michigan removes lifetime ban on food stamps for people with drug convictions.