Prescription Drug Advisory Boards: Who is Impacted and How to get Involved
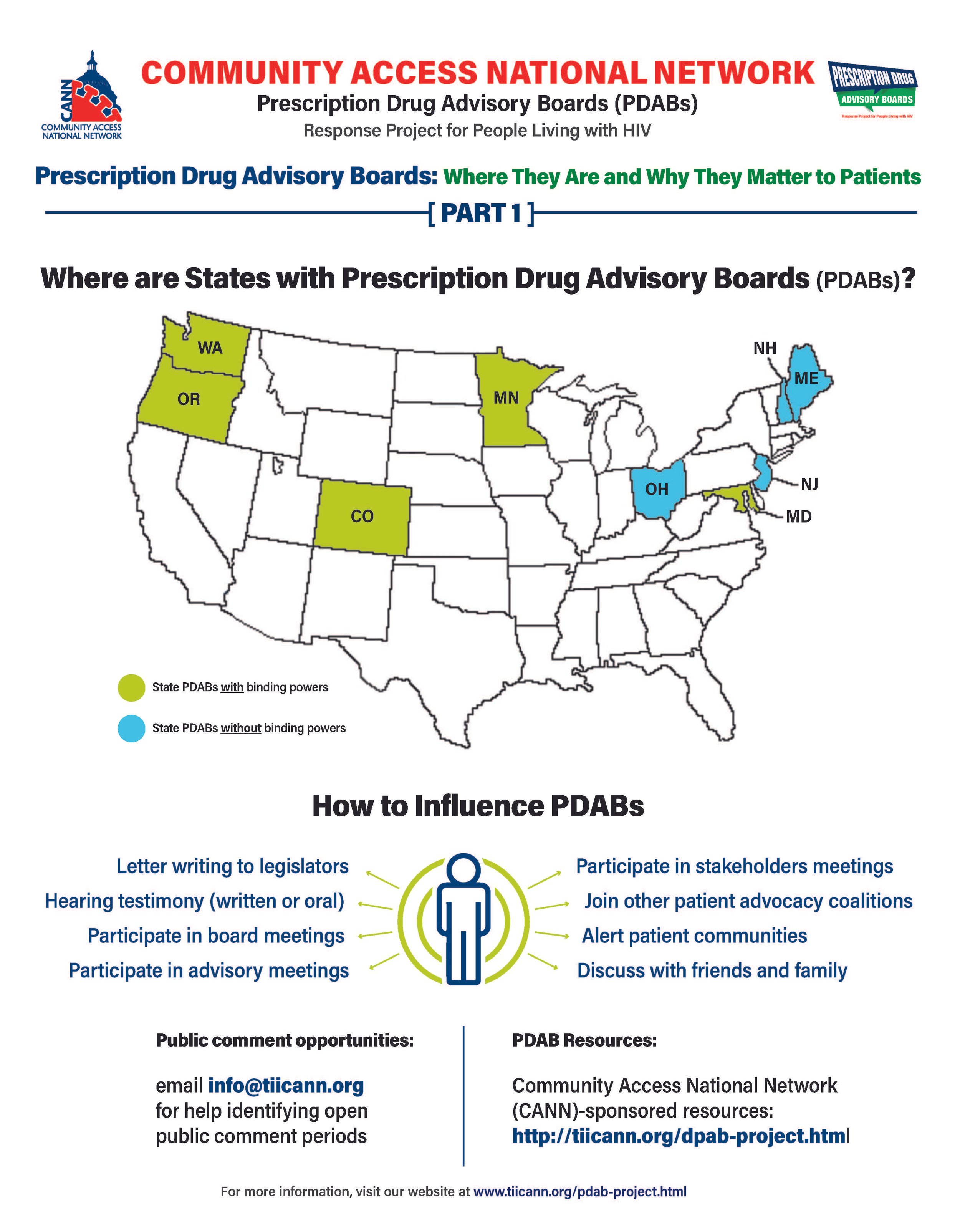
The prescription drug advisory board (PDAB) train keeps chugging along. Presently, there are nine (9) states that had, have or are in the process of enacting PDAB legislation: Washington, Oregon, Colorado, Michigan, Minnesota, New Jersey, New Hampshire, Maryland, and Maine. Ohio, it would seem, has abandoned their PDAB efforts. Their geographical variance reflects the diversity of their structures. Some of the boards have five members, and some have seven. While all are appointed by the governor, they differ regarding which departments they are associated with. For example, Colorado’s is associated with the Division of Insurance, and Oregon’s is associated with the Department of Consumer and Business Services.
The assortment of structure does not stop at department association. The number of drugs to be selected annually for review also varies, such as Colorado with five and Oregon with nine. Even the number of advisory council members lacks consistency. The New Jersey DPAB advisory council has twenty-seven (27) members, while Colorado’s has fifteen (15). Inconsistency in structure means inconsistency in operations. Thus, the help or harm patients ultimately receive will vary drastically from state to state. The most important differences are the powers bestowed upon the various DPABs. In addition to shaping many policy recommendations, five (5) currently have the ability to enact binding upper payment limit (UPL) settings: Washington, Oregon, Colorado, Maryland, and Minnesota.
An upper payment limit sets a maximum for all purchases and payments for expensive drugs. By setting UPLs for high-cost medications, improved ability to finance treatment equals greater access to high-cost medicines. A UPL sets a ceiling on what a payor may reimburse for a drug, including public health plans, like Medicaid.
Patients, advocates, caregivers, and providers are concerned about PDABs because the outcomes of theory versus practice can have dire consequences. Theoretically, PDABs should reduce what patients spend out of pocket for medications and lower government prescription drug expenditures. However, the varied ways different PDABs are set to operate could jeopardize goals. Focusing on lowering reimbursement rates could affect the funds used as a lifeline by organizations benefiting from the 340B pricing program even while not meaningfully reducing patient out-of-pocket costs. If reimbursement limits are set too low, those entities will have drastic reductions in the funding they use for services for the vulnerable populations they serve. UPLs could ultimately increase patients' financial burden if payers increase cost-sharing and change formulary tiers to offset profit loss from pricing changes or institute utilization management practices like step-therapy or prior authorization. Increasing patient administrative burden necessarily decreases access to medication. When patients are made to spend more time arguing for the medication they and their provider have determined to be the best suited for them, rather than simply being able to access the medication, the more likely patients are to have to miss work to fight for the medication they need or make multiple pharmacy trips – or suffer the health and financial consequences of having to “fail” a different medication first. PDAB changes could affect provider reimbursement, which could be lowered with pervasive pricing changes. Decreased provider reimbursement could result in additional costs being passed onto patients or, in the situation of 340B, safety-net providers, reduce available funding for support services patients have come to rely upon.
The divergent factors that different PDABs use for decision-making are of concern as well. It is not enough to just look at the list price of drugs and the number of people using them. For example, some worthwhile criteria for consideration of affordability challenges codified in Oregon’s PDAB legislation are: “Whether the prescription drug has led to health inequities in communities of color… The impact on patient access to the drug considering standard prescription drug benefit designs in health insurance plans offered…The relative financial impacts to health, medical or social services costs as can be quantified and compared to the costs of existing therapeutic alternatives…”. But few of these PDABs consider payer-related issues like limited in-network pharmacies, discriminatory reimbursement, patient steering mechanisms, or frequency of utilization management as hindrances to patients getting our medications.
Effectively seeking and considering input from patients, caregivers, and frontline healthcare providers is also of concern. The legislation of various DPABs specifies the conflicts of interest that board members cannot have and must disclose. Some even have appointed alternates to allow board members to recuse themselves from making decisions on drugs with which they have financial and ethical conflicts. However, most of the advisory boards are providers, government, and otherwise industry-related. The board members are even required to have advanced degrees and experience in health economics, administration, and more. The majority of the discourse is not weighted towards the patient and our advocates. Few, if any, specific active outreach measures when it comes to seeking patient input. For example, the Ryan White HIV/AIDS Program requires patient and community engagement outlets in planning activities. But no PDAB legislation, to our knowledge, requires PDABs to engage with these established patient-oriented consortia. We know well in HIV that expecting already burdened patients often struggle to meet limit engagement opportunities from government boards – we know the very best practices are going to patients, rather than expecting patients to come to these boards. Beyond these limited engagement opportunities and failure to reach out to spaces where patients are already engaged, some states have exceptionally short periods in which to gather these inputs.
However, depending on the individual state’s DPAB structure, there is an opportunity for patients, caregivers, and organizations to give input through public comment periods and particular meetings aimed at stakeholder engagement. For states considering PDAB legislation, like Michigan, patients can and should engage in the legislative process. One place to keep abreast of different state’s PDAB activities is the Community Access National Network’s PDAB microsite. The microsite has an interactive map where you can access various states’ PDAB sites as they are created. States with fully formed PDABs have sites that display their scheduled meetings, previous decisions made, agendas for future sessions, and, most notably, details of the process for the public to provide input. Most of the meetings are open to the public, with the public invited to provide oral public comment or to submit written comments. Attending meetings and speaking directly to the boards is a way to have board members and others hear directly from those who will be affected by their decisions. Written public comment is also essential, especially from community patient advocacy organizations. Some DPABS also provide access to virtual meetings where stakeholders can provide feedback and input.
Medicare has six protected drug classes: anticonvulsants, antidepressants, antineoplastics, antipsychotics, antiretrovirals, and immunosuppressants. This means that Medicare Part D formularies must include them but that protection exists because we know how important these medications are. Antiretrovirals and oncology medications are a part of that list because adversely affecting the mechanisms of access to those drug classes is life-threatening to those who need them. It is imperative that continued scrutiny be placed upon DPABs to ensure that their benefits are patient-focused, like reducing administrative burden and barriers to care, rather than a mask that ultimately benefits payers by increasing their profits.